Players often decide within seconds whether a game feels intuitive or confusing. UI is the quiet force behind that moment. It guides the player’s eyes, shapes their understanding, and sets the rhythm of how they move through the world. Even the most polished environments lose impact when the UI feels cluttered or unclear.
Most teams run into similar challenges as development grows. Screens become crowded. The visual language drifts from one feature to another. Navigation slows down because the experience never fully formed around player needs. UI can end up working, but not truly supporting the game.
UI matters because it defines how players read mechanics, absorb feedback, and feel confident in every action. It connects design with understanding, and when done well, it keeps players immersed without calling attention to itself.
In this article of Polydin Game art studio, I explore the essential principles of game UI design, the elements that shape how players interact with a game, and the practical workflow behind creating clear and reliable interfaces. The goal is to show how thoughtful UI turns complexity into clarity and helps games feel more welcoming from the very first moment.

Need Game
Art Services?
Visit our Game Art Service page to see how
we can help bring your ideas to life!
What Is UI in Video Games?
Game UI is the visual and interactive layer that helps players understand a game’s systems. It includes menus, icons, HUD elements, inventories, dialogue screens, and any visual cue that explains what the game expects from the player.
UI shapes how a game feels from the moment it starts. Opening an inventory, scanning a minimap, reading ability cooldowns, or navigating a quest log all rely on UI. If these moments feel confusing, the entire experience becomes harder than it should be.
UI plays a core role in clarity and immersion. Good UI communicates without overwhelming. It supports worldbuilding by using colors, shapes, and animation that match the tone of the game. In recent years, UI has evolved from static menus to dynamic and sometimes fully diegetic interfaces that blend into the world. Players expect cleaner layouts, faster navigation, and interfaces that understand their intent instead of slowing them down.
What Are Game UI Elements?
These components shape how players navigate the world and understand every action the game offers.
- Menus
- HUD components
- Inventory screens
- Dialogue boxes
- Skill trees
- Notifications and prompts
Each element carries its own logic and emotional tone. A dialogue box can set the mood of an entire conversation. A notification can either reassure the player or interrupt them. A skill tree can inspire creativity or frustration depending on how readable it is.
HUD (Heads-Up Display)
Purpose of HUD
HUD delivers instant information without pulling players out of the moment. It is the bridge between situational awareness and immersion.
HUD Placement and Design Principles
HUD design is a balance between clarity and subtlety. Safe zones keep important details readable. Clutter reduction prevents overwhelm. Some games use dynamic HUDs that fade or shift based on context, while others stick to static layouts for predictability. Knowing when to show information and when to hide it is part of thoughtful UI work.
How to Create an Excellent Game UI Design
User Research and Planning
Every strong UI starts with understanding how players behave. Watching how they move through menus or struggle with a game mechanic often reveals more than any document. Early planning also means understanding platform needs. UI that works on PC may feel cramped on a handheld device. Setting usability goals at the start helps the art and design teams stay aligned.
Wireframing and Prototyping
Low fidelity layouts give you the freedom to experiment before committing to visuals. At this stage, it is all about structure. Mapping how players move between screens forces you to think like them rather than like a designer. Rapid iteration keeps the team honest, because early ideas are often revised once you see real players interact with them.
Visual Design
This is where UI gains personality. Color, typography, iconography, and hierarchy all shape the mood. A sci-fi shooter will not share the same UI tone as a cozy RPG, even if both use similar principles. Maintaining consistency is essential. Players rely on patterns to navigate without thinking. Readability also matters across devices, so UI must hold up on different resolutions, lighting setups, and display sizes.
Testing and Iteration
Fresh eyes are invaluable. A player who has never seen the game reveals gaps the team has grown used to. Accessibility is part of this stage. Text size, colorblind support, scalable UI, and simple controls help more players enjoy the experience. Iteration relies on both qualitative reactions and measurable data. Patterns matter, but feedback should inform outcomes rather than dictate them.
Developer Handoff
Once the UI is ready for integration, the process shifts to clarity and organization. Export-ready assets, clean naming, and clear documentation help the team avoid mistakes. Good handoff is not about making huge manuals. It is about giving developers what they need without slowing them down. Tools and workflows differ across engines, but smooth collaboration keeps UI consistent throughout the build.
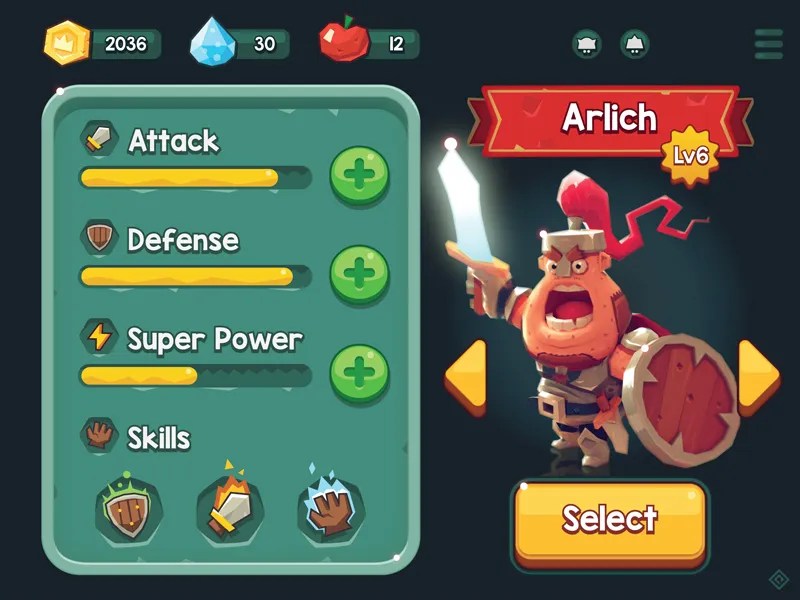
Examples of Great Game UI in Action
- Persona 5 Royal
A bold, stylish UI that treats every screen as part of the world’s personality. It proves UI can be both informative and expressive.
- Halo Infinite
Clear, readable HUD with strong spatial awareness. It supports fast pacing without distracting from combat.
- Pokémon Series
Simple, accessible menus that make complex systems feel approachable for players of all ages.
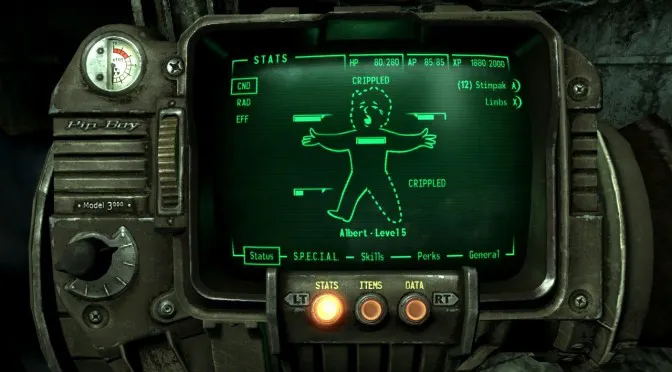
- Fallout Series
Diegetic UI through the Pip-Boy adds worldbuilding while still providing deep information.
- League of Legends
A competitive UI built around precision and clarity. Every icon, cooldown, and visual cue supports decision making.
- The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
A UI that blends into a large world while still offering clean navigation, readable inventories, and scalable information.
Benefits of Good UI in Games
Good UI feels invisible. It supports emotional connection, helps players understand systems, and keeps them focused on the world rather than fighting the controls.
- Stronger immersion and emotional connection
- Better player understanding and guidance
- Higher accessibility
- Reduced cognitive load
- Smoother progression and retention
When UI is done well, players feel confident and in control. When it is done poorly, the entire game feels heavier than it should.
Conclusion
Game UI sits between creativity and clarity. It shapes how players learn, navigate, and grow comfortable inside a game’s systems. From early planning to visual design and final integration, each step of UI development influences how the experience feels moment to moment. Strong UI does not try to impress the player. It simply supports them in every decision.
UI is more than buttons and menus. It is how players think, feel, and interact with your world. A well designed interface strengthens trust and turns learning curves into natural flow. Thoughtful UI gives players confidence. It keeps them moving without hesitation. It quietly elevates everything else the team builds.
FAQs
What are the 4 types of game UI?
Non-Diegetic
This is the UI that sits outside the game world. Health bars, ammo counters, minimaps, and most HUD elements fall into this category. Players depend on it because it delivers quick information without needing any in-world explanation.
Diegetic
Diegetic UI exists inside the game’s world and is visible to both the player and the character. The Pip-Boy in Fallout or the holographic displays in Dead Space are good examples. This type of UI strengthens immersion and feels like part of the storytelling.
Spatial
Spatial UI appears in the world but isn’t directly part of it. For example, an outline around an interactable object or a floating waypoint marker. Players see it in 3D space, but characters usually don’t. It helps bridge gameplay needs with environmental clarity.
Meta
Meta UI communicates the character’s status using stylized or symbolic effects. Screen edges turning red when health drops is a common example. It’s not part of the world, but it reflects the character’s condition and emotions in a way players instantly understand.
What is the difference between UI and UX in gaming?
UI is the visual layer players interact with. It’s the buttons, menus, icons, HUD elements, and all the visual signals that help them understand the game. UI focuses on what players see and touch.
UX is the overall experience of using those systems. It’s how smooth the navigation feels, how quickly players find what they need, how clear the information is, and how naturally everything flows. UX focuses on how players think and feel while interacting with the game.
A simple way to put it is that UI builds the interface, while UX shapes the journey. Good games rely on both working together.
What software is used to design game UIs?
Game UI is usually created with a mix of design tools and engine-based systems. Most studios start with layout and visual design tools like Figma, Adobe XD, Photoshop, Illustrator, or Sketch to shape the look and structure. These programs help build wireframes, mockups, icons, and visual styles before anything goes into the game.
Once the visuals are ready, teams bring the assets into engines such as Unity or Unreal Engine, where the UI becomes interactive. These engines handle logic, animation, transitions, navigation, and responsive behavior across different screen sizes.
Some teams also use tools like After Effects for motion prototypes or Spine for animated UI elements, depending on the style of the game.
The exact mix of tools changes from project to project, but the general workflow always starts with design software and ends inside the game engine where the UI comes to life.
Sources
Polydin uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
- “The Best Isometric RPGs in 2025.” Instant-Gaming, 2025, https://www.instant-gaming.com/en/blog/14080-the-best-isometric-rpgs-in-2025/. Instant-Gaming.com
- “What Is an Isometric Game.” Dreams Quest, 2025, https://www.dreams.quest/post/what-is-an-isometric-game. Dreams Quest
- “RPG General News – Best Isometric RPGs.” RPGWatch, 24 Mar. 2025, https://rpgwatch.com/forum/threads/rpg-general-news-best-isometric-rpgs.62309/. RPGWatch
- “Aside from Fallout, What’s Your Favourite Isometric RPG?” No Mutants Allowed, 6 Dec. 2018, https://www.nma-fallout.com/threads/aside-from-fallout-whats-your-favourite-isometric-rpg.216966/



