Welcome to the world of Game HUD Design, where the convergence of functionality and visual finesse plays a pivotal role in enhancing players’ gaming experiences. The HUD, or Heads-Up Display, is a vital communication bridge between the virtual world and the player, providing essential information, feedback, and control elements in real time.
In this article by Polydin game art outsourcing studio, we will delve into the fundamentals of HUD design, exploring its core elements, various interface types, the significance of customization, and how to tailor it effectively for different gaming platforms. So, whether you’re a seasoned game developer seeking to perfect your HUD designs or an aspiring designer eager to create immersive user interfaces, join us on this journey to unravel the secrets behind a compelling and seamlessly integrated HUD experience.
What is Game HUD Design?

HUD, an acronym for Heads-Up Display, is a critical graphical overlay in video games that provides essential information, feedback, and interactive elements to players directly on the screen. It bridges the game’s virtual world and the player, delivering crucial details about the game state, character status, inventory, maps, health, ammunition, and much more in real time.
Game HUD design is planned carefully to ensure that players can access vital information at a glance, without the need for extensive navigation through menus or pausing the game. A well-crafted game HUD design not only enhances the overall gaming experience but also contributes to the immersion and engagement of players, helping them stay informed and in control throughout their gameplay journey.
What are the Elements of HUD in Games?

The elements of game HUD Design can vary depending on the genre, style, and complexity of the game, but some common elements can be found in many games:
- Health and Stamina Bars: These bars display the player character’s current health and stamina levels, indicating their remaining vitality and ability to perform actions.
- Ammo and Weapon Information: This shows the number of ammunition rounds available for the player’s equipped weapon and the selected weapon or item.
- Minimap and Map: The minimap provides an overview of the game world, while the full map allows players to navigate and plan their routes.
- Objective Tracker: This element keeps track of current objectives, quests, or missions, helping players focus on their goals.
- Score and Points: Displayed to track the player’s score, points, or achievements, providing a sense of accomplishment.
- Inventory and Equipment: Allow players to manage their items, gear, and equipment during the game.
- Compass: Provides directional indicators, helping players find their way around the game world.
- Timers and Countdowns: Displays time-related information, such as countdowns for time-limited events or progress timers.
- Dialogues and Character Interactions: Shows conversations and interactions with non-player characters.
- Currency: Indicates the player’s in-game currency or resources.
- Status Effects: Notifying players of any positive or negative effects affecting their character.
Effective HUD design ensures that these elements are presented in a clear and intuitive manner, allowing players to quickly gather information without distraction or confusion, ultimately contributing to a seamless and enjoyable gaming experience.
HUD Interface Types
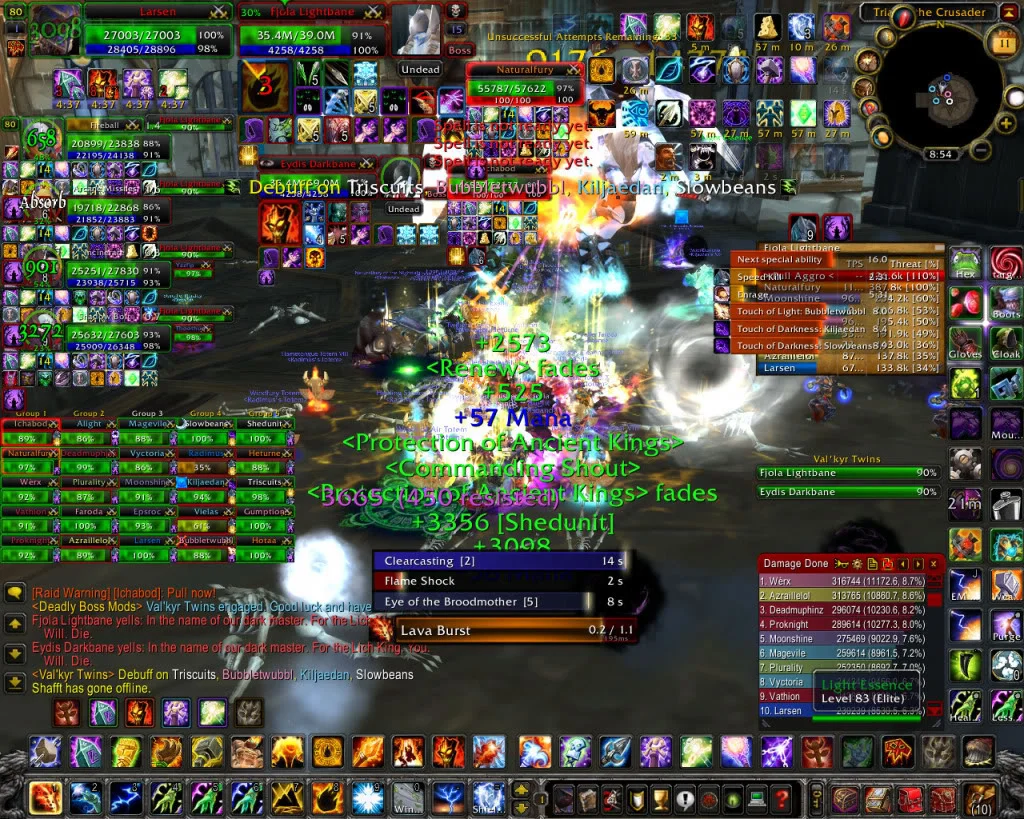
HUD (Heads-Up Display) interface types can vary based on the game’s genre, complexity, and intended user experience. Here are some common HUD interface types found in games:
- Minimalist HUD: This type of game HUD design aims to keep the on-screen elements simple and unobtrusive. It typically displays only essential information, such as health, ammo, and a minimalistic minimap, providing players with an immersive experience.
- Full-Screen HUD: Some games utilize a full-screen HUD, where all relevant information and interface elements cover the entire screen. This can be useful in games with complex mechanics or strategic elements, as it ensures players have all the necessary details at their disposal.
- Contextual HUD: In a contextual HUD, elements are displayed dynamically, appearing only when needed and disappearing when irrelevant. This approach prevents screen clutter and maintains focus on the gameplay.
- Immersive HUD: This type of game HUD design is designed to blend seamlessly with the game world, enhancing immersion. Information is integrated into the game environment, such as showing objectives on in-game signs or displaying health on the character’s armor.
- Customizable HUD: Many games offer players the option to customize their HUD, allowing them to choose which elements to display, their positions, and transparency levels. This empowers players to tailor the interface to their preferences.
- Augmented Reality (AR) HUD: Emerging in AR and VR games, this type of HUD overlays digital information onto the player’s real-world environment, creating a more immersive and interactive experience.
- Dynamic HUD: In dynamic HUDs, the appearance and layout of elements change based on the game’s context. For example, the health bar might change color or size if a character takes damage.
- Retro HUD: Some games pay homage to older video games by using a retro-inspired HUD design with pixel art and nostalgic fonts, evoking a sense of nostalgia for players.
The choice of HUD interface type depends on the game’s aesthetics, game mechanics, and target audience. A good game HUD design enhances the player’s experience by providing essential information that is visually appealing and intuitive.
The Importance of HUD Customization
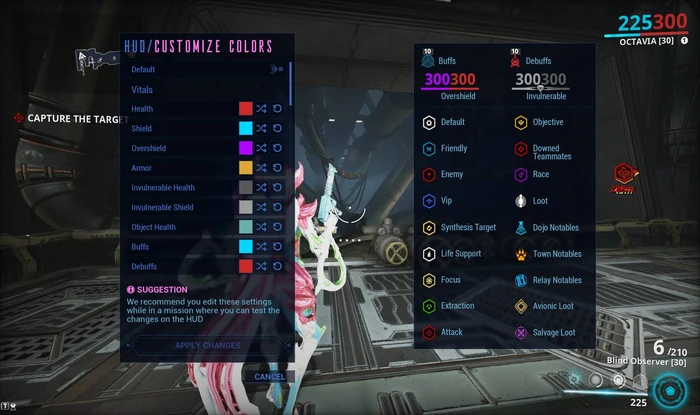
HUD customization plays a pivotal role in modern game design and game HUD design, allowing players to personalize their gaming experience according to their preferences and needs. The importance of HUD customization lies in its ability to enhance player immersion, accessibility, and overall satisfaction. By allowing players to adjust the on-screen interface to suit their individual playstyle, developers can create a more inclusive and enjoyable experience for a diverse audience.
Firstly, HUD customization empowers players to tailor the interface to their liking, which can significantly improve immersion. By choosing what information is displayed, its position, size, and transparency, players can create a HUD that seamlessly integrates with the game world, reducing distractions and enhancing the feeling of being fully immersed in the virtual environment.
Secondly, customization enhances accessibility for players with different needs and preferences. Some players may require larger text or icons for better visibility, while others might prefer a minimalistic HUD to minimize screen clutter. By accommodating these individual preferences, game developers can ensure their games are accessible and enjoyable to a broader audience.
Furthermore, HUD customization adds an element of control and personalization to the gaming experience. Players feel more connected to the game when they can make it their own. This sense of agency can increase player engagement and longer play sessions.
In summary, HUD customization is a vital aspect of modern game design. By allowing players to personalize their on-screen interface, developers can enhance immersion, accessibility, and overall player satisfaction. Customizable HUDs create a more inclusive and enjoyable experience, catering to individual preferences and playstyles and ultimately enriching the gaming journey for all players.
What is the Difference Between UI and HUD?

The key difference between UI (User Interface) and HUD (Heads-Up Display) lies in their scope and purpose within a video game.
User Interface (UI) refers to the entire set of on-screen elements that players interact with to navigate the game, access menus, manage inventory, and perform various in-game actions. The UI encompasses everything from the main menu, character inventories, health bars, maps, dialogue boxes, and more. It is a comprehensive system that facilitates communication between players and the game world, providing essential information and controls.
On the other hand, the Heads-Up Display (HUD) is a specific subset of the UI. It consists of real-time information and indicators superimposed on the gameplay screen without obstructing the player’s view. Common HUD elements include health and stamina bars, ammunition counters, minimaps, objective markers, and status notifications. The HUD is designed to provide crucial information to players during gameplay without requiring them to access separate menus or interfaces.
The UI encompasses all the game’s interactive elements, including menus, inventories, and in-game actions. At the same time, the HUD specifically refers to the real-time indicators and information displayed on the screen during gameplay. Both UI and HUD play essential roles in enhancing player experience and engagement, with the UI serving as the broader framework for player interaction and the HUD offering immediate and relevant feedback during gameplay.
Read Also: What is UI in Games?
What is the difference between HUD and HMD?
HUD stands for Heads-Up Display, while HMD stands for Head-Mounted Display. The primary difference between the two lies in their function and form of presentation:
- Heads-Up Display (HUD):
- HUD is a transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints.
- It overlays digital information onto the user’s field of view, typically within a vehicle’s windshield or a pilot’s visor, allowing users to access information while keeping their attention focused on the task at hand.
- HUDs are commonly used in automotive vehicles, aircraft, and certain video games to provide real-time information such as speed, navigation directions, and vital stats.
- Head-Mounted Display (HMD):
- HMD is a wearable device that users place directly on their heads, covering their eyes or surrounding them with screens or lenses to create immersive visual experiences.
- HMDs are commonly used in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, where they immerse users in simulated environments or overlay digital content onto their real-world surroundings.
- Unlike HUDs, HMDs completely block or alter the user’s view of the physical world, providing a fully immersive experience rather than overlaying information onto the existing environment.
In summary, HUDs provide a non-intrusive way to display information within the user’s field of view, while HMDs offer immersive visual experiences by surrounding users with virtual or augmented content.
Games With The Most Creative HUD Implementation
The games listed below showcase exemplary creativity in their Heads-Up Display (HUD) implementations, enhancing the gaming experience through innovative design and functionality:
- Dead Space
Known for its immersive approach, Dead Space integrates the HUD seamlessly into the game environment, presenting vital information such as health and ammunition via in-universe holographic displays on the protagonist’s suit.
- NieR: Automata
This game employs a minimalistic HUD design that adapts dynamically based on the situation, providing essential information while maintaining immersion. The HUD elements blend well with the game’s aesthetic and contribute to its overall atmosphere.
- Shadow Of the Colossus
In this game, the HUD is intentionally kept minimalistic to emphasize the game’s minimalist and immersive world. Essential information is displayed contextually, ensuring players remain engaged without distraction.
- The Metro Series
With its post-apocalyptic setting, The Metro Series utilizes a HUD that reflects the game’s gritty and immersive world. The HUD elements are designed to feel integrated into the protagonist’s equipment, like his watch and gas mask, enhancing realism.
- The Assassin’s Creed series
Across various entries, the Assassin’s Creed series features HUD designs that adapt to the historical settings, providing relevant information while maintaining thematic consistency. The HUD elements blend seamlessly with the game’s environments, enhancing immersion.
- Horizon Zero Dawn
This game implements a dynamic HUD that adjusts based on the player’s actions and surroundings. The HUD elements provide essential information without cluttering the screen, contributing to the game’s immersive open-world experience.
How to Optimize the HUD for Different Platforms

Optimizing the game’s HUD design for different platforms is crucial to ensure a seamless and enjoyable gaming experience for players across various devices. Here are some key considerations to achieve effective HUD optimization:
Screen Size and Aspect Ratio
Different platforms like smartphones, tablets, PCs, and consoles have varying screen sizes and aspect ratios. Design the HUD elements to adapt and scale properly on each platform to avoid cropping, stretching, or distortion.
Touchscreen Interaction
For mobile devices with touchscreen controls, ensure that HUD elements are large enough to be easily tapped and interacted with using fingers. Prioritize essential controls and minimize clutter to avoid accidental taps.
Controller Support
Consider using physical controllers when designing for consoles or PCs. Ensure the HUD elements work well with gamepad inputs and provide clear visual cues for button prompts.
Platform-Specific Features
Take advantage of platform-specific features, like motion controls or touch gestures on certain devices. Tailor the HUD to enhance gameplay using these unique functionalities.
Performance Optimization
Optimize HUD elements to have minimal impact on performance, especially on lower-end devices. Keep the number of graphical elements in check and use efficient code to ensure smooth performance.
Customization Options
Allow players to customize the HUD to their preferences. Provide options to adjust element positions, transparency, and sizes, enabling players to create a personalized gaming experience.
Contextual Display
Implement a dynamic HUD that adapts based on the gameplay situation. Display information relevant to the current scenario, avoiding clutter and unnecessary distractions.
Test and Iterate
Perform thorough testing on each platform to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments. Gather feedback from players and iterate on the game’s HUD design to achieve the best possible user experience.
By carefully optimizing the HUD for different platforms, game developers can enhance the accessibility and playability of their games, catering to a diverse audience and ensuring a smooth gaming experience on various devices.
Rules of Game HUD Design
A game’s Heads-Up Display (HUD) is a critical element that conveys vital information to players while they engage with the game’s world. A well-designed HUD enhances the gaming experience by providing essential data without disrupting the player’s immersion. To achieve this balance, there are several fundamental rules of game HUD design that game developers and designers should follow:

1. Game HUD Design Should be Consistent with Theme and Style
A cohesive visual style and theme are vital for any game, and the HUD should reflect and enhance these aspects. The HUD’s aesthetics, including color schemes, fonts, and graphical elements, should harmonize with the game’s overall design. A medieval fantasy game, for example, might feature a HUD with ornate, medieval-inspired graphics, while a futuristic sci-fi game would opt for a sleek and futuristic HUD. Consistency in style ensures that the HUD feels like an integral part of the game world.
2. Strive for Maximum Clarity and Readability
The primary purpose of a game HUD is to communicate essential information clearly and quickly. To achieve this, designers must prioritize readability. This means using legible fonts, contrasting colors, and intuitive icons. The size and placement of HUD elements should be carefully considered to avoid clutter or obstructing the player’s view. Clarity and readability are especially crucial during fast-paced gameplay, where split-second decisions can determine success or failure.
3. Consider Smart Placement of HUD Elements
Strategic placement of HUD elements can significantly impact the player’s experience. Information that requires constant monitoring, like health, ammunition, or a minimap, should be located near the edges of the screen to minimize eye movement. Less critical information can be placed further from the center. This smart placement ensures that players can access essential data without taking their focus away from the game’s action.
4. Keep Your Game HUD Design on a “Need to Know” Basis
One of the challenges of game HUD design is balancing the amount of information displayed. While it’s essential to provide players with useful data, overloading the HUD with unnecessary information can overwhelm and confuse them. The principle of “need to know” should guide the inclusion of HUD elements. Display information that directly affects the player’s decisions and actions, such as health, ammunition, or objectives. Avoid cluttering the screen with superfluous data that doesn’t contribute to the gaming experience.
5. Make it Customizable Where You Can
Players have diverse preferences, and what works for one player may not suit another. Providing options for HUD customization can enhance the player experience. This might include allowing players to resize or reposition HUD elements, adjust transparency, or choose from different HUD layout presets. Customization empowers players to tailor the HUD to their liking, promoting a more personalized and enjoyable gaming experience.
Game HUD Design in Mobile Gaming
In the fast-paced world of mobile gaming, the Heads-Up Display (HUD) plays a critical role in providing players with essential information without cluttering the screen. Mobile game HUD design requires a delicate balance between functionality and an unobtrusive user interface to ensure an immersive gaming experience on smaller screens.
Key Considerations for Mobile Game HUD Design
- Screen Real Estate: With limited space on mobile screens, prioritizing crucial information is essential. Designers must ensure that the HUD elements do not obstruct the player’s view while maintaining easy accessibility.
- Touch Controls: Mobile games heavily rely on touch controls, impacting HUD design. Buttons and icons should be appropriately sized and spaced to accommodate touch gestures, minimizing the risk of accidental inputs.
- Adaptability Across Devices: The diversity in mobile devices necessitates a responsive design that adapts to various screen sizes and resolutions. A well-designed HUD should remain effective and visually appealing across a range of devices.
- Contextual Information: Displaying context-sensitive information is crucial. The HUD should dynamically adjust based on the game’s state, providing relevant details without overwhelming the player.
- Aesthetic Consistency: Maintaining a consistent visual style ensures coherence in the gaming experience. The HUD elements should align with the overall art direction of the game, contributing to a seamless and polished presentation.
Tools for Game HUD Design
Creating an effective HUD involves leveraging specialized tools tailored for game design. Here are some widely used tools:
- Adobe Illustrator: Illustrator’s vector-based capabilities make it a popular choice for creating scalable and detailed HUD elements. Its precision and versatility facilitate the design of icons, buttons, and other graphical elements.
- Sketch: Sketch is known for its user interface and user experience (UI/UX) design features. It’s well-suited for designing mobile-friendly HUDs, allowing designers to create and iterate on layouts quickly.
- Unity UI: For game developers working in Unity, the built-in Unity UI system provides a powerful platform for creating interactive HUD elements. It seamlessly integrates with Unity’s game development environment.
- Figma: Figma is a collaborative design tool that enables real-time collaboration on game design projects. It’s particularly useful for teams working on HUD designs, allowing for efficient collaboration and feedback.
What are Some Creative Alternatives for Integrated HUD Elements?
Traditional HUDs (Heads-Up Displays) can sometimes clutter the screen or break immersion. To keep players immersed while still delivering vital information, developers have embraced more integrated and creative UI solutions:
- Diegetic UI: This is UI that exists in the game world. Think of the holographic health bar on Isaac’s spine in Dead Space, or ammo counters projected onto weapons in Crysis. Players read the interface as part of the environment, not as a screen overlay.
- Environmental Feedback: Games like Journey or Shadow of the Colossus use animation, color shifts, and environmental cues to signal player status or objectives. Light dimming, heartbeat sounds, or camera shake can subtly replace health bars or alerts.
- Character-Based Cues: Visual damage on the character model (like limping or bloody clothes), or behavioral cues like labored breathing, can communicate player condition naturally; Red Dead Redemption 2 and The Last of Us excel here.
- Audio-Driven UI: Sound cues, music changes, or voice lines can replace visual UI. Hellblade: Senua’s Sacrifice uses binaural audio to convey danger and guidance, enhancing immersion without cluttering the screen.
What are the Key Components of a Comprehensive Game UI Beyond the HUD?
While the HUD gets the most attention, a game’s full UI includes a wide system of player interactions. Key components include:
- Menus & Navigation Systems: This includes main menus, pause screens, inventory systems, and skill trees. Smooth navigation is critical for usability and pacing. Modern RPGs like Horizon: Forbidden West or Diablo IV invest heavily here.
- Dialogue & Choice Interfaces: In narrative-driven games, dialogue trees and decision prompts shape player agency. These must be both readable and emotionally engaging; see Mass Effect or Disco Elysium for strong examples.
- Tutorial & Onboarding UI: Contextual prompts, button hints, or ghost inputs help players learn controls and mechanics. Great onboarding is invisible yet effective; Celeste and Portal are masters of this.
- Accessibility Features: Customizable text size, colorblind modes, and remappable controls ensure inclusivity. AAA games like The Last of Us Part II raised the bar for comprehensive accessibility UI.
- Feedback & Microinteractions: Hit markers, loot pop-ups, crafting notifications; these reinforce action and reward. When finely tuned, they make the game feel responsive and alive.
Methodologies and Scientific Approach to Game HUD Design
Effective HUD design often involves a blend of creativity and a scientific approach. Here are methodologies to enhance the design process:
- User-Centered Design:
- Prioritize user experience by involving players in the design process. Collect feedback through playtesting and iterate on the HUD design based on user preferences and behavior.
- Eye Tracking Studies:
- Conduct eye tracking studies to understand where players naturally focus during gameplay. This data can inform the placement of critical HUD elements to ensure they capture the player’s attention at the right moments.
- Usability Testing:
- Perform usability tests to evaluate how easily players can interpret and interact with the HUD. Identify potential pain points and refine the design to enhance overall usability.
- Data-Driven Iteration:
Analyze gameplay data to gain insights into player behavior. Use this information to refine the HUD design iteratively, ensuring that it aligns with player preferences and enhances the overall gaming experience.
Advanced Techniques for Gameplay HUD Design
Here are some advanced techniques for gameplay HUD design:
- Minimalism and Clutter Reduction: Embrace minimalism in HUD design by prioritizing essential information and reducing visual clutter. Use clean layouts, concise text, and unobtrusive graphics to ensure that the HUD enhances rather than distracts from gameplay.
- Customizable HUD Elements: Implement customizable HUD elements that allow players to personalize their interface based on their preferences and playstyle. Provide options to adjust the size, position, opacity, and visibility of HUD elements to accommodate different screen resolutions and player preferences.
- Dynamic Contextual Display: Design HUD elements to adapt dynamically based on the context of the gameplay. Display relevant information only when needed, such as health bars appearing during combat or objective markers appearing when relevant goals are nearby, to avoid overwhelming the player with unnecessary information.
- Visual Hierarchy and Grouping: Establish a clear visual hierarchy and grouping of HUD elements to guide players’ attention and facilitate quick and intuitive information retrieval. Use color, size, and spacing to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary elements, ensuring that essential information stands out prominently.
- Interactive and Reactive Elements: Incorporate interactive and reactive HUD elements that respond to player input and in-game events. For example, health bars may flash red when critical health is low, or objective markers may pulse or animate to draw attention to important objectives.
- Contextual Feedback and Notifications: Provide contextual feedback and notifications through the HUD to inform players of important events, milestones, or achievements. Use icons, animations, and sound cues to convey information quickly and intuitively without interrupting gameplay flow.
- HUD Customization Options: Offer robust customization options for the HUD that allow players to tailor the interface to their preferences and accessibility needs. Provide settings to adjust colors, fonts, transparency, and layout, as well as options to enable or disable specific HUD elements based on individual preferences.
- Adaptive HUD Scaling: Implement adaptive HUD scaling to ensure that the interface remains readable and usable across different screen sizes and aspect ratios. Use responsive design principles to adjust the layout and sizing of HUD elements dynamically based on the display resolution and device specifications.
- Multiplayer and Co-op Integration: Design HUD elements to accommodate multiplayer and cooperative gameplay scenarios, where multiple players may share the same screen or have overlapping HUD elements. Ensure that the HUD remains clear and informative for all players, regardless of their role or perspective.
- Accessibility Considerations: Prioritize accessibility in HUD design by ensuring that all players, including those with disabilities, can easily navigate and understand the interface. Provide options for text size, color contrast, and audio cues, as well as alternative input methods for players with mobility or dexterity limitations.
Tailoring Gameplay HUDs for Different Genres
- First-Person Shooter (FPS): FPS games typically feature minimalistic HUDs that prioritize essential information such as health, ammo, and weapon status. Display weapon reticles, ammo counters, and minimaps discreetly to maintain immersion while providing critical gameplay feedback.
- Role-Playing Game (RPG): RPGs often have complex HUDs that display a wide range of information, including character stats, inventory items, quest objectives, and world maps. Design RPG HUDs with customizable layouts and contextual tooltips to accommodate diverse player preferences and playstyles.
- Real-Time Strategy (RTS): RTS games require HUDs that facilitate strategic decision-making and resource management. Include elements such as minimaps, unit status bars, and resource counters that provide players with essential information at a glance while allowing for precise control and micromanagement.
- Platformer: Platformer games benefit from HUDs that are unobtrusive yet informative, providing players with feedback on character status, level progress, and collectible items. Use visual cues such as character animations and level design to convey information naturally, minimizing the need for explicit HUD elements.
- Racing: Racing games often feature dynamic HUDs that display information such as speed, lap times, and position relative to other racers. Design racing HUDs with customizable layouts and color-coded indicators that enhance visibility and readability while maintaining focus on the fast-paced action.
- Adventure: Adventure games may require HUDs that adapt to different gameplay scenarios, such as puzzle-solving, exploration, and dialogue interactions. Design versatile HUDs with contextual overlays and tooltips that provide players with relevant information based on their current objectives and actions.
By tailoring HUD design to the specific requirements and conventions of each genre, developers can create immersive and intuitive user interfaces that enhance the gameplay experience and contribute to overall player satisfaction.
What is the difference between HUD and GUI in games?
In video games, HUD (Heads-Up Display) and GUI (Graphical User Interface) serve distinct purposes, although they may sometimes overlap.
- HUD: The HUD is a specific type of display that presents critical information directly related to gameplay without obstructing the action on screen. It typically includes elements such as health bars, ammunition counts, minimaps, and other real-time stats that players need to make quick decisions during gameplay. The HUD is designed to be minimalistic and unobtrusive, allowing players to focus on the game itself while still keeping them informed.
- GUI: The GUI, on the other hand, encompasses all interactive visual elements within a game that facilitate player interaction and navigation. This includes menus, inventory screens, settings, and other elements that players engage with outside of the core gameplay experience. While the HUD provides immediate information during play, the GUI often includes more comprehensive interfaces for managing game mechanics, such as character customization or level selection.
In essence, the HUD is a subset of the GUI, specifically focused on real-time information during gameplay, whereas the GUI covers all interactive elements within the game.
What are the advantages of heads-up display?
The Heads-Up Display (HUD) offers several advantages in gaming, enhancing the player’s experience and improving gameplay efficiency:
- Real-Time Information: HUDs provide players with immediate access to crucial information, such as health, ammo, and objectives. This allows players to make informed decisions quickly, which is vital in fast-paced games.
- Enhanced Immersion: By integrating relevant information seamlessly into the gameplay experience, HUDs help maintain immersion. Players can remain focused on the game world without having to pause or navigate through menus to check their stats.
- Space Efficiency: HUDs are designed to occupy minimal screen space while presenting essential data. This efficient use of screen real estate prevents clutter, ensuring that the gameplay area remains clear and unobstructed.
- Visual Feedback: Many HUDs incorporate visual indicators, such as color changes or animations, to provide feedback on player actions. For instance, a flashing health bar can indicate low health, prompting players to take action.
- Customization: Many modern games allow players to customize HUD elements, enabling them to prioritize the information most relevant to their play style. This flexibility enhances user experience by catering to individual preferences.
Final words
In conclusion, HUD design shapes the player’s gaming experience by providing essential information and interactions during gameplay. The elements of a well-designed HUD should be intuitive, unobtrusive, and tailored to the specific needs of each game and platform. HUD customization gives players a more personalized experience, making them feel more engaged with the game.
Understanding the difference between UI and HUD is crucial for creating a cohesive and seamless user interface that enhances gameplay. Moreover, optimizing the HUD for different platforms ensures players enjoy the game on various devices without compromising functionality or visual appeal. As game developers continue to innovate and cater to diverse audiences, thoughtful and efficient HUD design will remain a key aspect in shaping the success of modern video games.



