3D modeling vs sculpting are two different approaches to creating 3D objects and characters for various industries. While both techniques are used to create 3D assets, they differ in terms of methodology, workflow, purpose, and output. In this article by Polydin game art outsourcing studio, we will explore the differences between 3D modeling vs sculpting, their uses, advantages, and disadvantages, and help you determine which technique is better suited for your project.
What Is 3D Modeling?
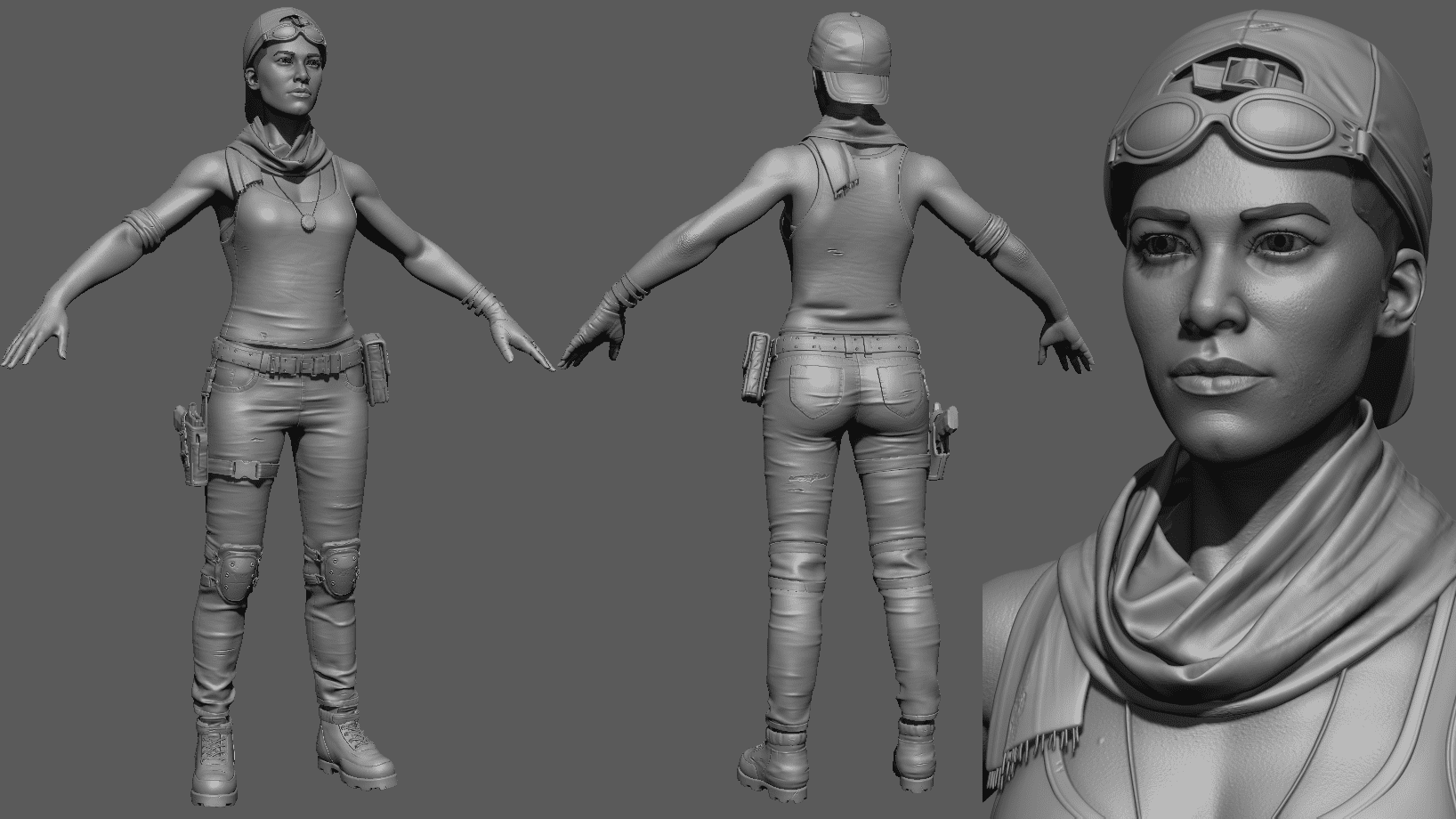
3D modeling is the process of creating a digital representation of a physical object or character using specialized software. The object is created by adding and manipulating digital shapes, edges, vertices, and textures in a virtual 3D space. The result is a three-dimensional model that can be viewed and animated from any angle.
Usage Of 3D Modeling
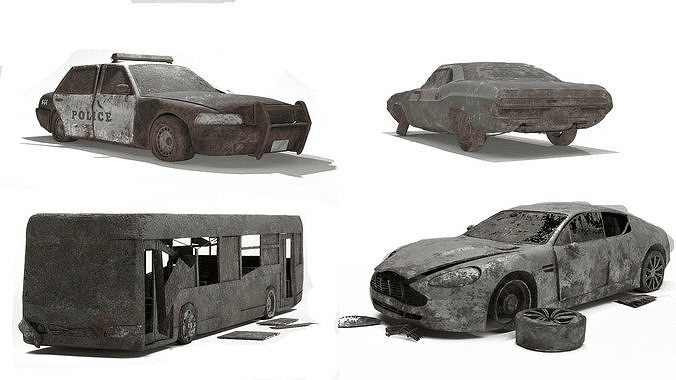
3D modeling is widely used in various industries, such as architecture, engineering, product design, and entertainment. In architecture and engineering, 3D models are used to create detailed building plans, simulate lighting, and design landscapes. In product design, 3D models are used to create prototypes, test designs, and visualize product concepts. In entertainment, 3D models are used to create animated films, video games, and special effects.
What Is 3D Sculpting?
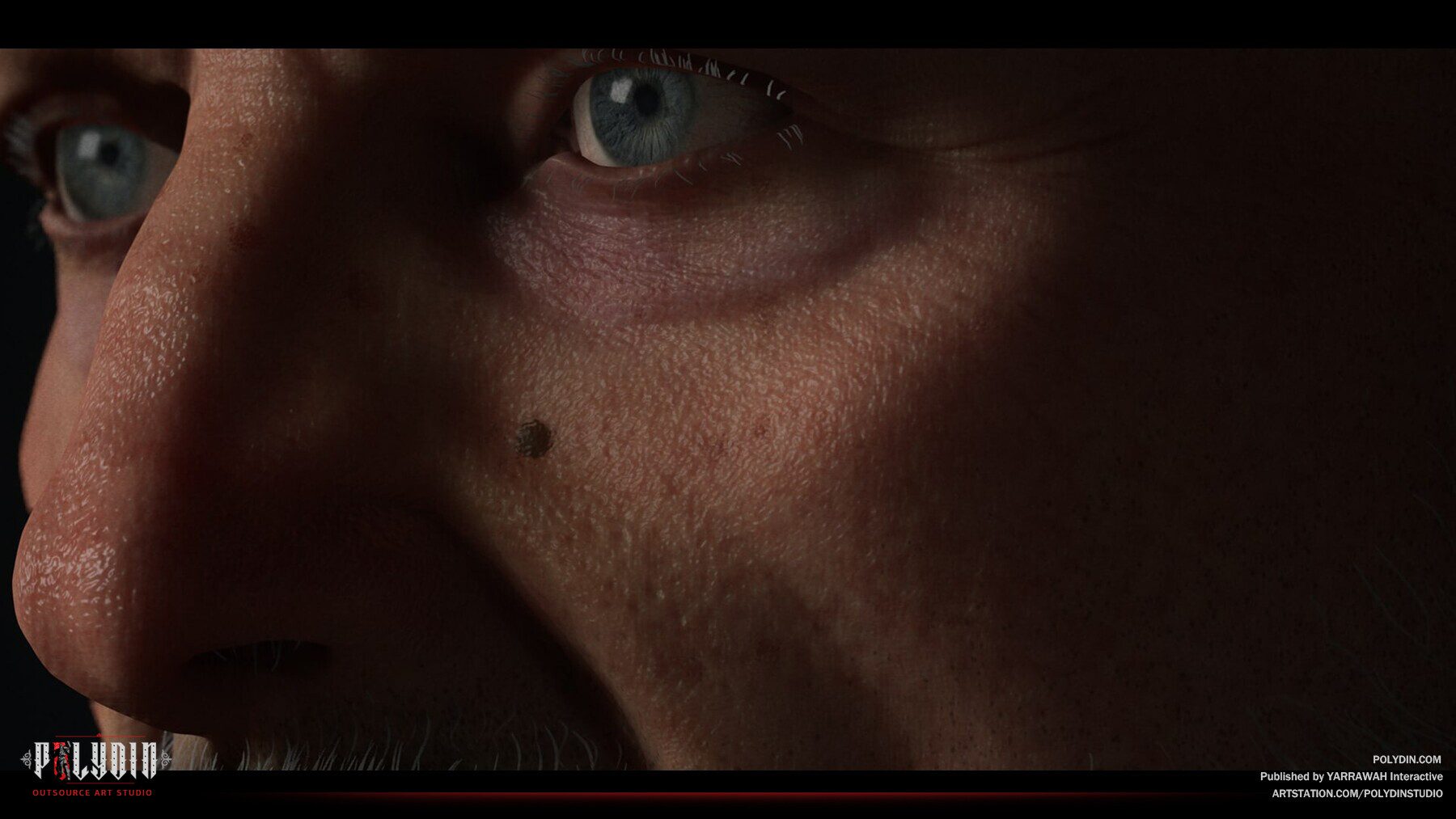

3D sculpting, also known as digital sculpting, is a technique used to create organic and highly detailed models using specialized software. Unlike 3D modeling, which relies on geometric shapes and edges to create objects, 3D sculpting works by directly manipulating a digital surface using tools that simulate real-world sculpting tools like brushes, knives, and chisels.
Usage Of 3d Sculpting
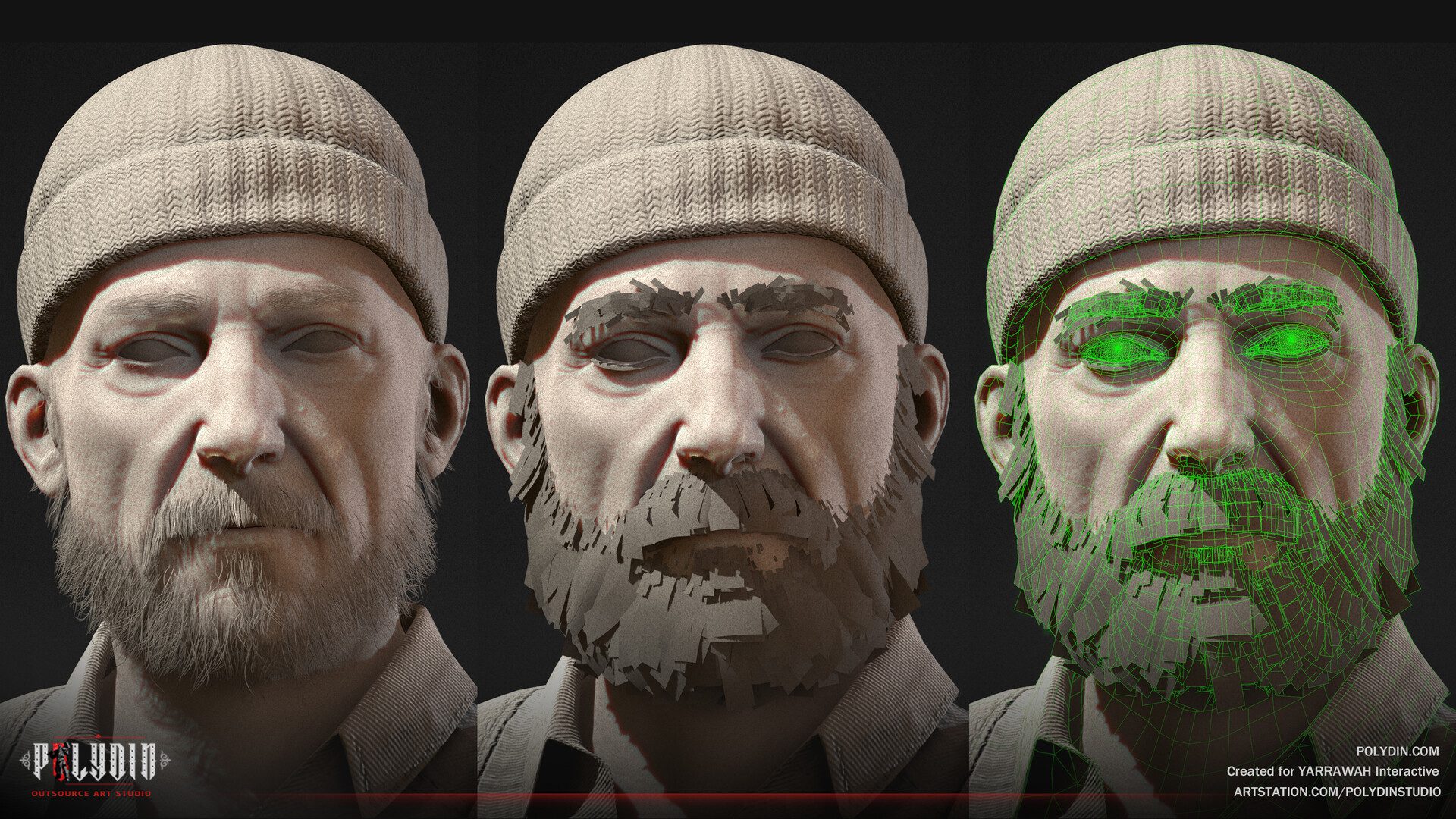

3D sculpting is widely used in film and television, video games, and product design industries. It is particularly useful for creating organic and highly detailed models such as characters, creatures, and landscapes.
Which Is the Better Option: 3D Modeling Or Sculpting?
Whether 3D modeling vs sculpting is the better option depends on the project’s specific needs and the artist’s preferences and skills. Both techniques have their own unique advantages and limitations.
3D modeling is typically better suited for creating geometric shapes, mechanical objects, and hard surface models. It relies on mathematical algorithms to create precise shapes and surfaces and is well-suited for creating objects that require accuracy and precision. 3D modeling is also often used in industries such as engineering and architecture, where accuracy and measurements are crucial.
On the other hand, 3D sculpting is better suited for creating organic and highly detailed models such as characters, creatures, and landscapes. It allows artists to work with virtual clay, adding and removing material to create intricate details, folds, and textures. 3D sculpting is a more artistic and intuitive approach to creating 3D assets. It allows artists to express their creativity and imagination in a way that is not possible with traditional 3D modeling techniques.
Ultimately, the choice between 3D modeling vs sculpting depends on the project requirements and the artist’s skills and preferences. In some cases, a combination of both techniques may be necessary to achieve the desired results.
3D Modeling VS Sculpting | What’s the Difference?
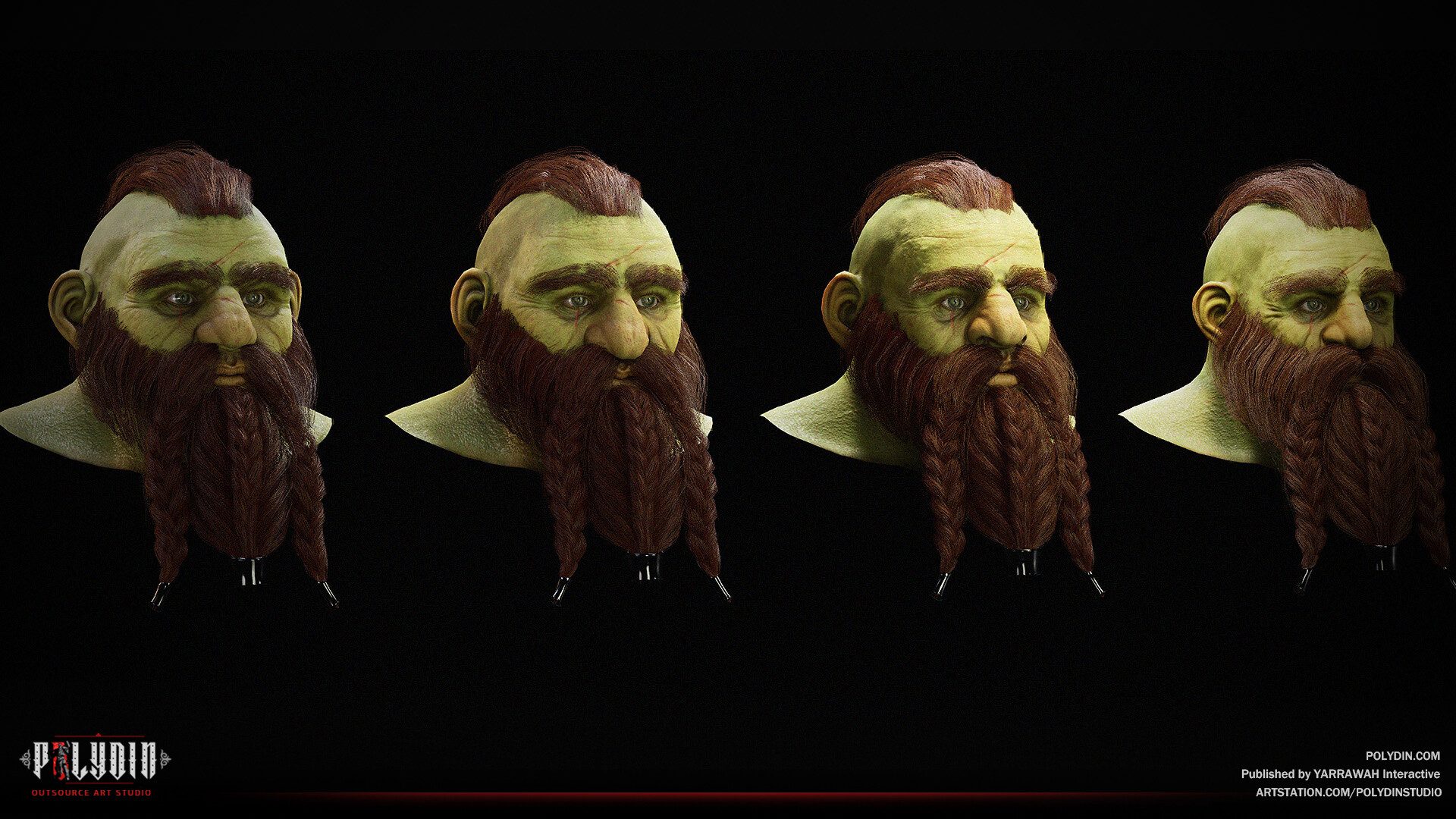

When it comes to the differences of 3D modeling vs sculpting, the keyword is “technicality vs artistry”. But let’s get to specifics and see how they differ in different areas:
Methodology
3D modeling is a technique that uses mathematical algorithms to create a 3D object by defining its shape and surface. It involves creating a 3D model from scratch by starting with a basic shape and then adding or subtracting elements to create the desired object. Sculpting, on the other hand, is a more artistic approach that involves working with a virtual clay-like material to create a 3D object by shaping and molding it.
Workflow
The workflow for 3D modeling typically involves creating a basic shape or wireframe, adding more detail, and then applying textures and materials to the surface. Sculpting, on the other hand, typically involves starting with a basic shape and then refining the details until the desired level of detail is achieved.
Purpose
The purpose of 3D modeling is to create precise and accurate representations of objects, while sculpting is used to create highly detailed and organic shapes. 3D modeling is often used in industries such as architecture, engineering, and product design, while sculpting is commonly used in the entertainment industry for character and creature creation.
Learning Curve
3D modeling typically has a steeper learning curve than sculpting, which involves understanding mathematical concepts such as topology and geometry. Sculpting, on the other hand, relies more on artistic skills such as sculpting and painting, making it more intuitive for artists with a traditional art background.
Output
The output of 3D modeling is typically a clean and precise object with defined edges and surfaces, while sculpting produces highly detailed and organic shapes with intricate details and textures.
Speed
3D modeling is typically faster than sculpting, as it relies on mathematical algorithms to create objects. Sculpting, on the other hand, can be time-consuming, as it involves adding and refining details by hand.
Hardware
Both 3D modeling and sculpting require powerful hardware to run efficiently, but sculpting typically requires more advanced hardware due to the intensive processing power required to create highly detailed objects.
Pros and Cons of 3D Modeling
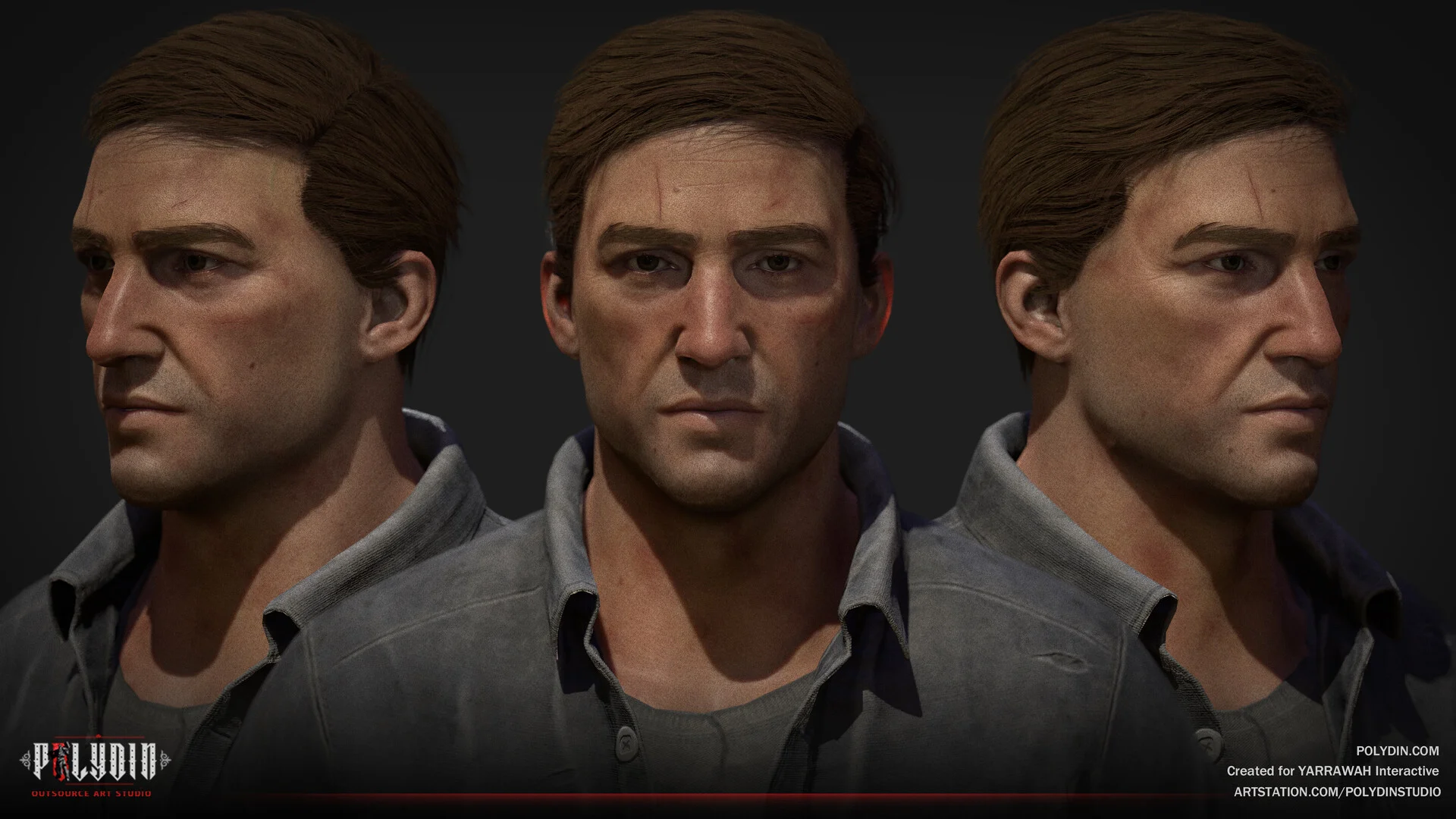

Pros and cons of 3D Modeling are as follows:
Pros of 3D Modeling:
- Realism: 3D models offer lifelike visuals, enhancing immersion and player engagement.
- Versatility: They allow dynamic camera angles and flexible animations for diverse gameplay experiences.
- Prototyping: Quick 3D prototypes facilitate iterative design, saving time and resources.
- Future-Proofing: High-quality 3D assets can be reused or enhanced for sequels and expansions.
- Market Demand: Many players expect modern games to have 3D graphics, expanding the target audience.
Cons of 3D Modeling:
- Complexity: Creating and animating 3D models requires specialized skills and tools, increasing development costs.
- Performance: Resource-intensive 3D assets may hinder performance on lower-end devices.
- Learning Curve: Training artists and designers for 3D modeling can be time-consuming.
- Asset Size: Large 3D files may lead to extended loading times and storage demands.
- Artistic Limitations: Realism-focused designs may lack the charm and simplicity of 2D counterparts.
Pros and Cons of Sculpting
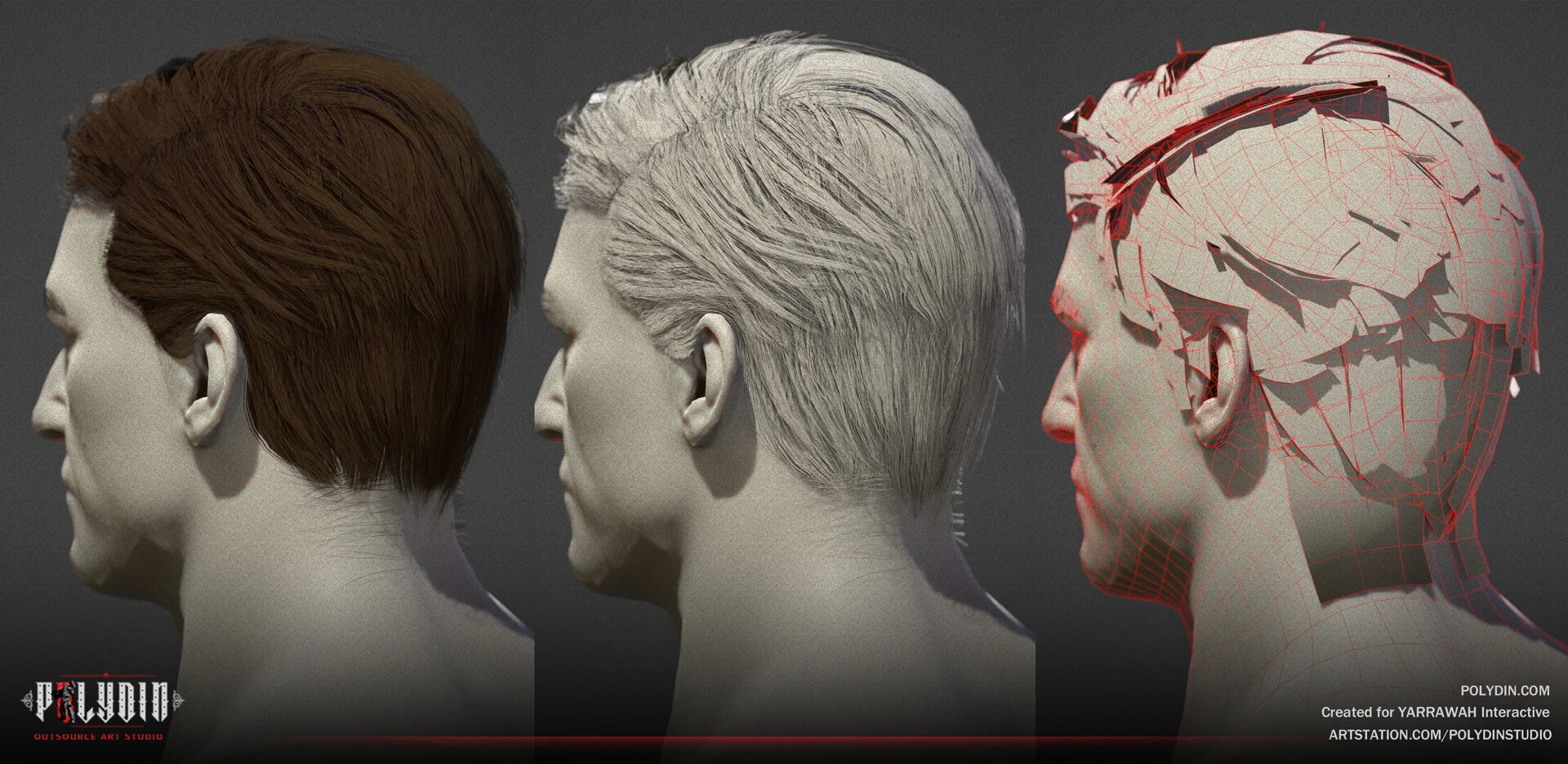

Pros of Sculpting:
- Realistic Details: Sculpting allows artists to create intricate and lifelike details in 3D models.
- Organic Shapes: It excels at crafting natural and organic shapes, ideal for characters and creatures.
- Artistic Freedom: Sculpting software provides a more intuitive and expressive approach to modeling.
- High-Quality Textures: Sculpted models can generate high-resolution textures for realistic surfaces.
- Seamless Integration: Sculpted assets can easily blend with other 3D elements, improving overall visuals.
Cons of Sculpting:
- Time-Consuming: Sculpting intricate details can be time-consuming, lengthening development cycles.
- Learning Curve: Mastering sculpting tools and techniques requires dedication and practice.
- Resource-Intensive: High-polygon sculpted models may strain system resources during rendering.
- Inflexible Edits: Major changes to sculpted models can be challenging and may require starting over.
- Not Ideal for Some Assets: Hard-edged or mechanical objects may be better suited for traditional 3D modeling techniques.
The Historical Development of 3D Sculpting Techniques and Tools
The origins of 3D sculpting can be traced back to the early days of computer graphics in the 1960s and 1970s when researchers began exploring ways to digitally model and manipulate three-dimensional objects. Initially, 3D sculpting involved primitive wireframe models and basic rendering techniques, limited by the computational power and graphical capabilities of early computers. However, with the advent of more powerful hardware and software in the 1980s and 1990s, 3D sculpting tools began to evolve rapidly, paving the way for more sophisticated modeling techniques.
The introduction of commercial 3D modeling software such as Autodesk’s Maya, 3ds Max, and Blender revolutionized the field of 3D sculpting, providing artists with powerful tools and workflows for creating complex and realistic digital sculptures. These software packages offered a range of sculpting tools, including polygonal modeling, subdivision surfaces, and digital sculpting brushes, enabling artists to sculpt organic shapes and intricate details with precision and ease. Additionally, advancements in hardware technology, such as the development of graphics processing units (GPUs) and multi-core processors, further accelerated the growth of 3D sculpting by improving rendering speeds and increasing computational performance.
What Software is Used for 3D Modeling?
Various software options are available for 3D modeling, catering to different needs and skill levels. Autodesk’s Maya and 3ds Max are widely used in the entertainment industry, offering comprehensive modeling and animation capabilities. Blender, a popular free and open-source option, provides a full-fledged 3D creation suite. Cinema 4D by Maxon targets motion graphics and visual effects. ZBrush is renowned for its powerful sculpting features. SketchUp is user-friendly and often used in architecture and design. Modo is known for its flexible modeling and rendering tools. Overall, artists can choose from a diverse range of 3D modeling software based on their specific project requirements and expertise.
What Software is Used for 3D Sculpting?

Popular 3D sculpting software includes ZBrush, known for its powerful sculpting, texturing, and painting tools, and Blender, a free and versatile open-source option. Autodesk offers Mudbox, ideal for detailed models and texturing. Sculptris, also from Pixologic, suits beginners with its user-friendly interface. 3D-Coat covers sculpting, retopology, UV mapping, and texturing. Maya by Autodesk, primarily an animation and modeling tool, includes sculpting features. Substance Painter, mainly a texturing tool, also has basic sculpting capabilities. Modo offers both modeling and sculpting tools. The choice depends on the artist’s needs and preferences, as each software has its strengths and specialties.
How Advancements in Technology Have Shaped the Evolution of 3D Sculpting
Advancements in technology have played a pivotal role in shaping the evolution of 3D sculpting, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in digital artistry. The introduction of digital sculpting software, such as Pixologic’s ZBrush, marked a significant milestone in 3D sculpting, offering artists powerful tools for sculpting highly detailed and organic forms directly in a digital environment. ZBrush introduced groundbreaking features like dynamic tessellation, sculpting layers, and advanced brush presets, empowering artists to create lifelike characters, creatures, and environments with unparalleled realism and fidelity.
Furthermore, the rise of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the way artists approach sculpting, providing a means to bring digital creations into the physical world. Artists can now sculpt intricate designs digitally and then print them out as physical objects using additive manufacturing techniques. This convergence of digital and physical sculpting has opened up new avenues for artistic expression and experimentation, blurring the lines between virtual and tangible art forms. As technology continues to advance, the future of 3D sculpting looks promising, with emerging technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) poised to redefine the creative process and expand the possibilities of digital sculpting even further.
What is VR Sculpting?
VR sculpting, also known as virtual reality sculpting, is a cutting-edge technique that utilizes virtual reality technology to create 3D models in a fully immersive environment. By donning a VR headset and using motion controllers, artists and designers can manipulate digital clay and other virtual materials in a three-dimensional space, much like traditional sculpting with physical tools. This method allows for a more intuitive and hands-on approach to 3D modeling, as it mimics the physical process of sculpting and enables the creator to view and interact with their work from any angle in real-time.
Key features of VR sculpting include:
- Immersive Environment: VR sculpting provides a highly immersive experience, making the artist feel as if they are working within the 3D space itself. This immersion helps with understanding the spatial relationships and proportions of the model.
- Intuitive Controls: Using motion controllers, artists can push, pull, carve, and manipulate virtual materials with precision, allowing for more natural and fluid movements compared to traditional 2D interfaces.
- Real-Time Feedback: Changes made to the model can be seen instantly from all angles, making it easier to spot and correct issues on the fly.
- Enhanced Creativity: The freedom to move around and interact with the model directly can inspire more creativity and innovation in the design process.
What are the Challenges of 3D Modeling?
3D modeling, while a powerful and versatile tool in various fields such as animation, game design, architecture, and product design, comes with its own set of challenges:
- Steep Learning Curve: Mastering 3D modeling software can be daunting for beginners due to the complexity of the tools and techniques involved. Understanding the interface, learning how to use different tools, and grasping the principles of 3D space and geometry require significant time and effort.
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in 3D modeling demands a solid understanding of technical concepts such as topology, UV mapping, rigging, and texturing. Without these skills, creating detailed and high-quality models can be challenging.
- High Computational Requirements: 3D modeling software often requires powerful hardware to handle complex models and renderings. High-resolution textures, detailed models, and advanced simulations can be taxing on even the most robust systems, leading to slow performance and long rendering times.
- Precision and Attention to Detail: Creating accurate and detailed models necessitates a high level of precision and meticulousness. Small errors in the modeling process can lead to significant issues later on, especially in animation or game development where models need to be both visually appealing and functional.
- Time-Consuming Process: Building high-quality 3D models is often a time-intensive process, involving multiple stages such as concept development, modeling, texturing, rigging, and rendering. Each stage requires careful attention and iteration, making the overall process lengthy.
- Keeping Up with Advancements: The field of 3D modeling is constantly evolving with new tools, techniques, and software updates. Staying current with the latest developments and continuously learning new skills is essential but can be overwhelming.
- Artistic and Technical Balance: Successful 3D modeling requires a blend of artistic talent and technical proficiency. Balancing the aesthetic aspects of design with the technical requirements of the modeling process can be challenging, especially for those who may be stronger in one area than the other.
Despite these challenges, advancements in technology and software are continually making 3D modeling more accessible and efficient, opening up new possibilities for artists and designers to bring their creative visions to life.
Final words
Both 3D modeling vs sculpting are powerful tools used in various industries for different purposes. 3D modeling is ideal for creating geometric shapes and objects, whereas 3D sculpting is better for creating organic and freeform designs. The choice between 3D modeling vs sculpting depends on the project’s requirements, the artist’s skill level, and the available software and hardware.
It’s essential to note that both methods require a certain level of proficiency and practice to master. With the right tools and training, artists can create stunning designs in either medium. Ultimately, the decision between 3D modeling vs sculpting comes down to the artist’s preference and the project’s specific needs.
Whether you’re creating a 3D model for architectural visualization or sculpting a character for a video game, choosing the right tool is crucial to achieving your desired outcome. By understanding the differences between 3D modeling vs sculpting, you can make an informed decision and produce outstanding 3D designs.



