In the dynamic world of computer graphics, 3D modeling and 3D rendering play pivotal roles in bringing virtual creations to life. 3D modeling involves crafting three-dimensional digital representations of objects, characters, or environments, while 3D rendering focuses on transforming these models into realistic, visually striking images. Understanding the distinctions between these two fundamental aspects of computer graphics is essential for anyone venturing into digital art, animation, video game development, architectural visualization, and beyond. This article by Polydin game art outsourcing studio, delves into the intricacies of 3D modeling and 3D rendering, exploring their unique functionalities, applications, and the creative synergy they foster.
What is 3D Modeling?
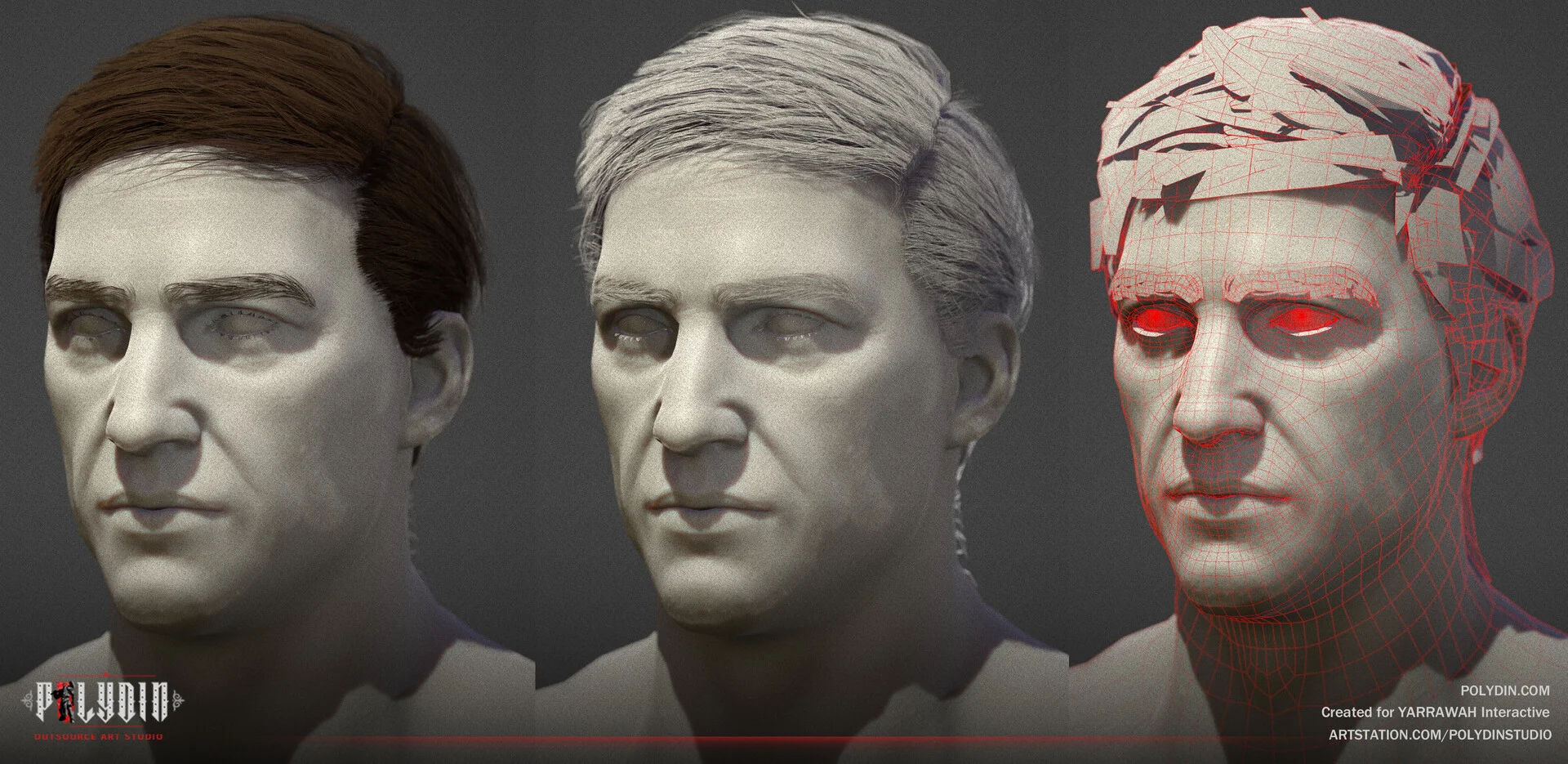

3D modeling is a digital art form and a fundamental technique in computer graphics that involves creating three-dimensional representations of objects, characters, environments, or any other imaginable form. In this process, artists and designers use specialized software to construct virtual models, giving them depth, volume, and shape.
These models can be as simple as geometric shapes or highly intricate, detailed structures, depending on the complexity of the desired end product. 3D modeling allows artists and developers to visualize and bring their ideas to life in a virtual space, making it an indispensable tool in various industries such as animation, video game development, film production, architectural design, product prototyping, and more.
What is 3D modeling Used For?

3D modeling is used across various industries and applications due to its versatility and ability to create lifelike representations of objects and scenes. In the realm of video games and animation, 3D modeling is essential for creating realistic characters, environments, and visual effects. It allows game developers and animators to craft immersive worlds that captivate players and viewers.
In architectural design, 3D modeling enables architects and designers to visualize and present their concepts in a more tangible and interactive way. It aids in creating detailed models of buildings and structures, helping clients and stakeholders better understand the proposed designs.
Furthermore, 3D modeling plays a crucial role in product design and manufacturing. Engineers and designers use it to create prototypes and visualize products before they are physically produced, saving time and resources in the development process.
In the film and entertainment industry, 3D modeling creates special effects, CGI characters, and detailed sets, enhancing the visual storytelling experience.
3D modeling is a powerful and essential tool that fuels creativity, innovation, and problem-solving across numerous fields, making it a cornerstone of modern digital art and design.
What IS 3D Rendering?
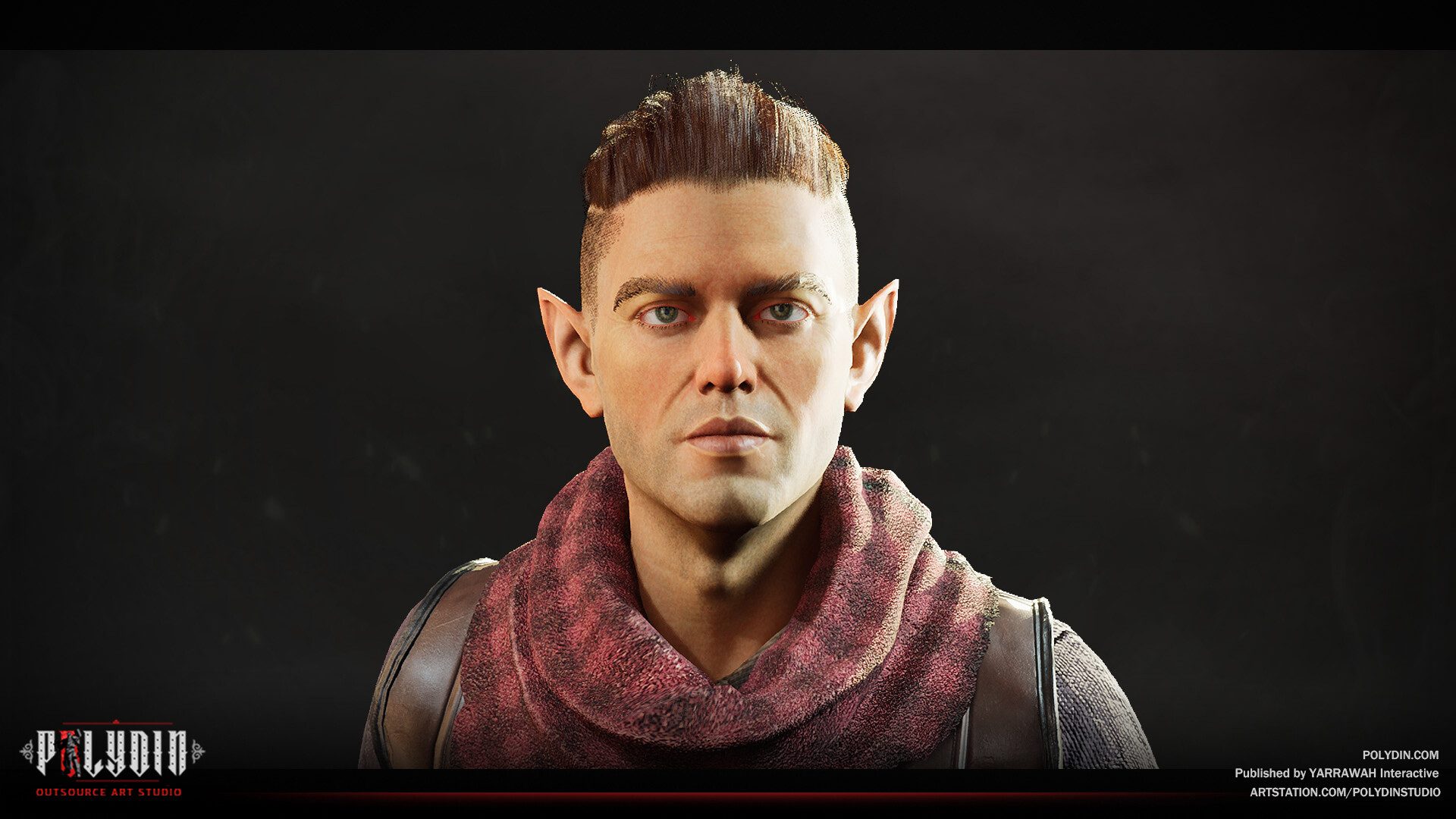

3D rendering is the process of converting a 3D model into a 2D image or sequence of images using specialized software and rendering techniques. It brings the virtual 3D objects and scenes to life, adding lighting, textures, shadows, and other visual effects to create a realistic or stylized representation of the 3D model.
The rendering process simulates the way light interacts with the objects in the scene, allowing for the calculation of reflections, refractions, and shadows. This results in lifelike imagery that can be used in various industries, such as video games, movies, architectural visualization, product design, and more.
3D rendering is a crucial step in final visual content production, as it transforms the raw 3D models into visually appealing and engaging images or animations. It enables artists, designers, and content creators to communicate their ideas and visions effectively, captivating audiences and immersing them in the virtual worlds they create.
What is 3D Rendering Used For?
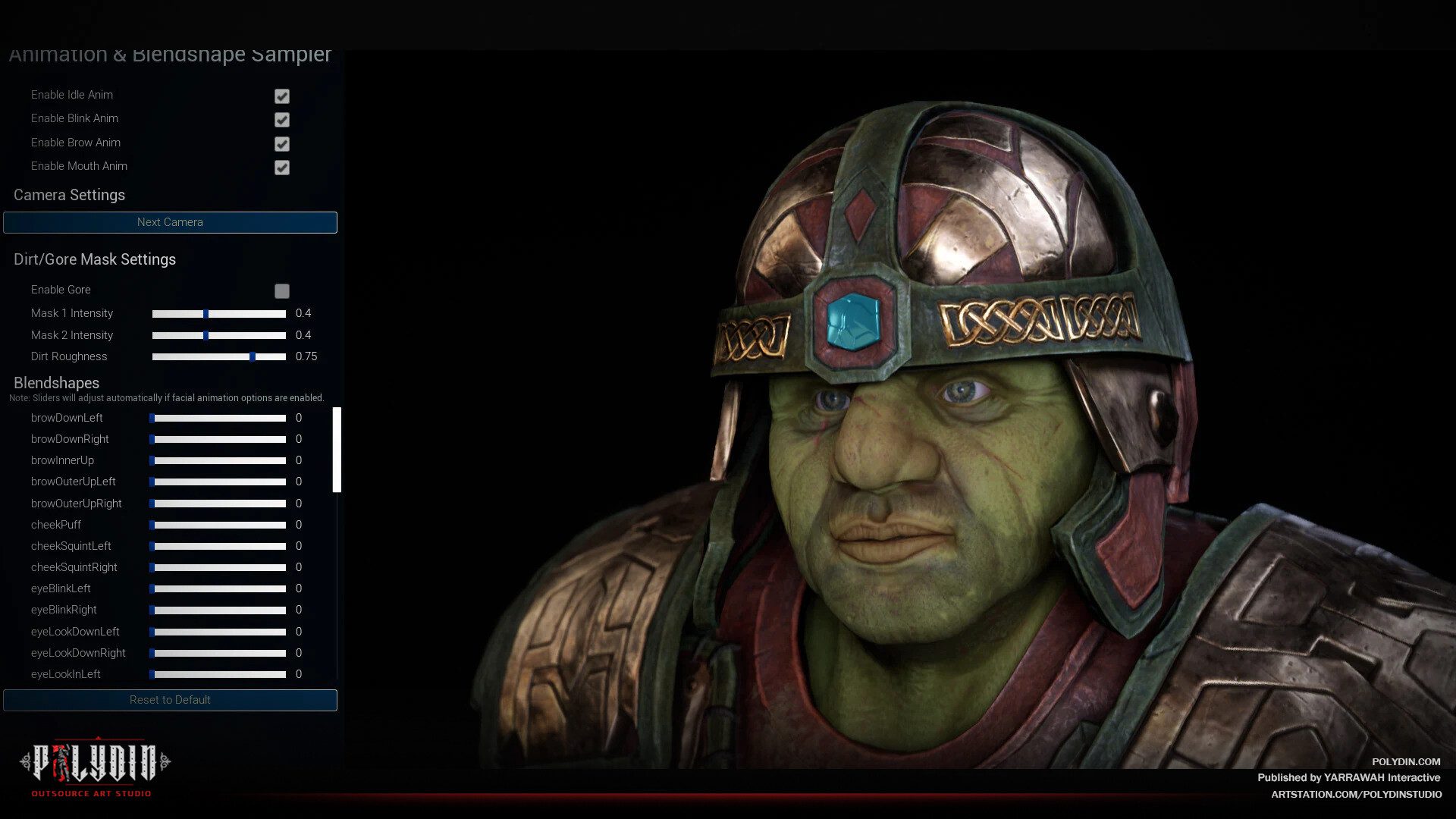
In the realm of video games and animation, 3D rendering takes detailed 3D models and transforms them into visually stunning and immersive experiences for players and viewers. It enhances the visual quality of characters, environments, and special effects, contributing to the overall appeal and realism of the final product.
In architectural visualization, 3D rendering enables architects and designers to showcase their projects photorealistic, providing clients and stakeholders with a clear and vivid representation of the proposed designs. It aids in creating compelling visual presentations that help communicate the project’s vision more effectively.
Moreover, in film and visual effects, 3D rendering is crucial to generating lifelike CGI elements, such as fantastical creatures, realistic explosions, and breathtaking landscapes, enriching the storytelling process and pushing the boundaries of creativity.
In summary, 3D rendering is a transformative process that elevates 3D models to their full potential, making them visually captivating and engaging in various industries, from entertainment and gaming to architecture and product design. It allows artists and designers to turn their imaginative concepts into stunning visuals, leaving a lasting impact on audiences worldwide.
Read Also: Types of Rendering Techniques | A Comprehensive Guide
What is the Difference Between 3D Modeling and 3D Rendering?
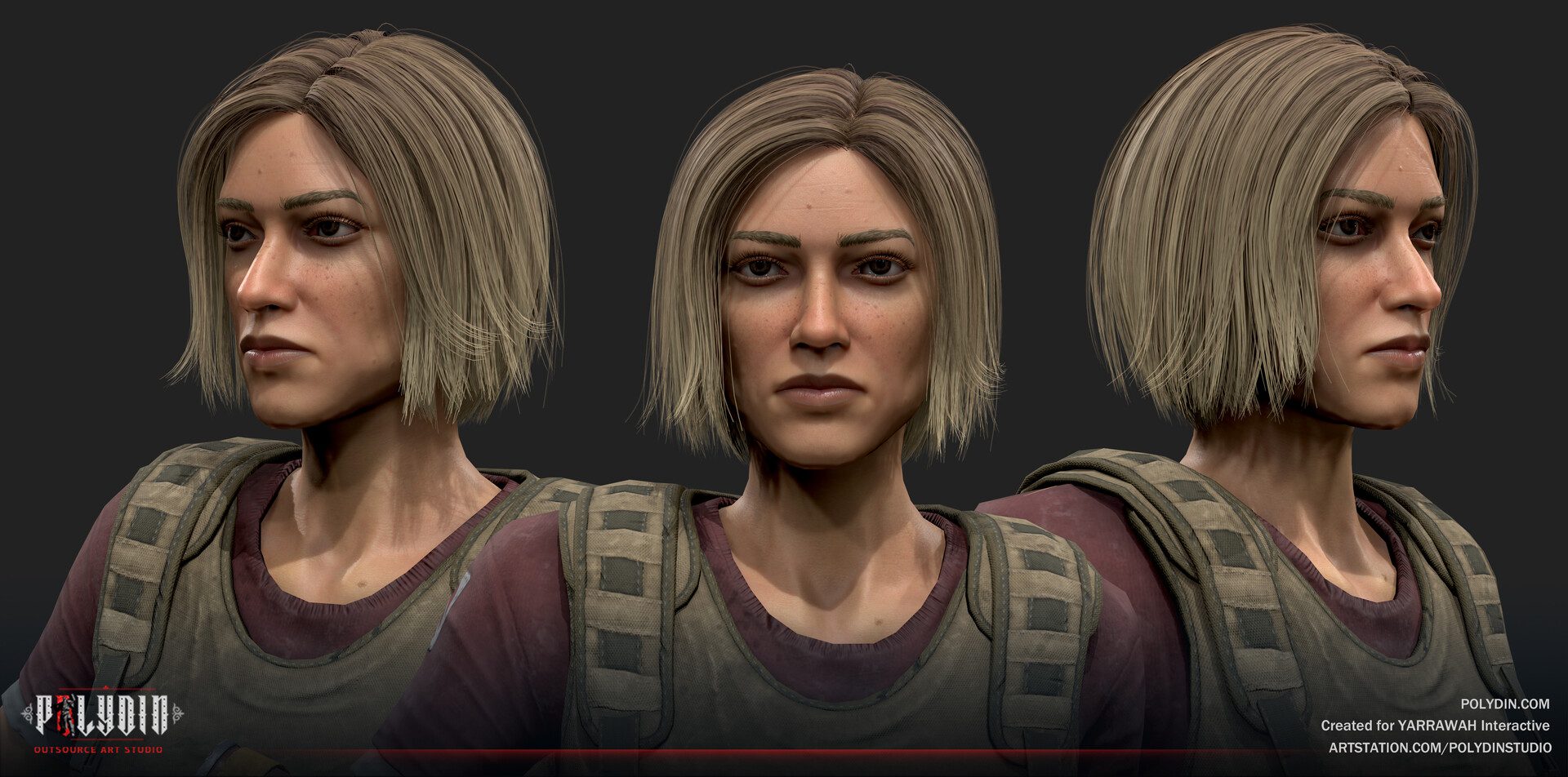

Regarding the world of 3D graphics and design, two terms that often surface are “3D modeling” and “3D rendering.” While they are interconnected, they serve distinct purposes in the creation of lifelike and captivating visuals. Understanding these essential processes’ differences is crucial for grasping the complete journey from concept to compelling 3D imagery. In this section, we will delve into the contrasting aspects of 3D modeling and 3D rendering, shedding light on how each contributes to the overall creative process and final output.
The Difference in Output
The primary difference between 3D modeling and 3D rendering lies in their respective outputs. 3D modeling is the initial step in creating a three-dimensional digital object or scene. It involves constructing the geometry, defining the shape, and setting the positions of the elements within the 3D space. The output of 3D modeling is a wireframe representation or a set of mathematical data that defines the object’s structure and appearance.
On the other hand, 3D rendering comes after the modeling process and focuses on transforming the raw 3D data into a visually realistic image. During rendering, lighting, shading, textures, and other visual effects are applied to the 3D model, simulating how light interacts with the surfaces to create a lifelike representation. The result of 3D rendering is a high-quality, detailed image or animation that appears almost photo-realistic, ready to be showcased in various media, such as video games, movies, or architectural visualizations. In summary, 3D modeling lays the foundation, while 3D rendering brings the model to life with stunning visual realism.
Techniques Used
The techniques employed in 3D modeling and 3D rendering differ significantly, reflecting their distinct roles in creation. In 3D modeling, artists construct and shape digital objects using various methods. These techniques include polygonal modeling, where objects are formed using connected vertices, edges, and faces; sculpting, which allows artists to manipulate the model’s shape like a virtual clay; and parametric modeling, enabling mathematical parameters to define the object’s features. Additionally, procedural modeling techniques automate the creation of certain complex structures.
In contrast, 3D rendering involves the application of advanced algorithms to simulate the interaction of light with the 3D model’s surfaces. Rendering techniques include ray tracing, which traces the path of light rays to create realistic lighting and reflections; global illumination, enhancing realism by considering indirect lighting effects; and rasterization, which converts the 3D data into 2D images through a process of pixel shading.
These rendering techniques and others contribute to achieving visually compelling and photorealistic images or animations, enhancing the overall quality and impact of the final output. By combining these techniques, 3D artists can create captivating visual experiences that blur the line between the virtual and the real world.
The Difference in Software
The distinction between 3D modeling and 3D rendering is also evident in the software used to perform these tasks. 3D modeling requires specialized software for artists and designers to build and manipulate digital objects and environments. Commonly used modeling software includes Autodesk Maya, Blender, 3ds Max, ZBrush, and Cinema 4D. These tools provide a wide array of features and tools tailored to the creative aspects of shaping and designing 3D models.
On the other hand, 3D rendering necessitates rendering software that focuses on generating high-quality images or animations from 3D models. Rendering software uses complex algorithms to simulate light interactions and produce visually appealing images. Prominent rendering software includes V-Ray, Arnold, RenderMan, Octane Render, and Blender’s Cycles. These rendering engines offer advanced features and optimizations to achieve realistic lighting, shading, and texturing, resulting in visually stunning and lifelike visualizations.
While some 3D modeling software includes basic rendering capabilities, dedicated 3D rendering software is essential for achieving the level of realism and sophistication required in animations, visual effects, and architectural visualizations. As such, both types of software play crucial roles in the 3D content creation pipeline, catering to the diverse needs and stages of the production process.
Creative Process vs. Technical Process
The difference between 3D modeling and 3D rendering also extends to the creative and technical processes involved. 3D modeling primarily revolves around the creative aspect of bringing ideas to life. It involves artists and designers using their imagination, artistic skills, and creativity to conceptualize and sculpt digital models of objects, characters, or environments. The creative process in 3D modeling focuses on achieving the desired look, shape, and form of the digital assets, often guided by artistic vision and design goals.
On the other hand, 3D rendering is more technically oriented and involves the process of generating realistic images or animations from the 3D models created during the modeling phase. It requires technical expertise in setting up lighting, materials, textures, and camera angles to achieve the desired visual outcome. Rendering also involves optimization techniques to ensure that the final output is visually appealing and computationally efficient.
In summary, while 3D modeling centers around the creative vision and artistic expression, 3D rendering focuses on the technical aspects of transforming those models into visually compelling and realistic representations. The creative and technical processes complement each other in the 3D content creation pipeline, resulting in the captivating visual experiences seen in video games, films, architectural visualizations, and other industries heavily relying on 3D content.
Flexibility
Flexibility is another key aspect that differentiates 3D modeling from 3D rendering. In the realm of 3D modeling, artists have the freedom to modify and manipulate digital assets extensively. They can adjust the models’ shapes, sizes, textures, colors, and other characteristics until they achieve the desired look and feel. This flexibility allows for iterations and changes throughout the creative process, allowing artists to refine their designs and explore various possibilities.
Conversely, 3D rendering is more rigid in making changes to the final output. Once the 3D models are rendered into images or animations, making significant alterations without re-rendering the entire scene becomes challenging. This limitation is due to the computationally intensive nature of rendering, which requires substantial processing power and time. As a result, the flexibility that exists during the modeling phase is not as readily available in the rendering stage.
Despite these differences in flexibility, both 3D modeling and 3D rendering are indispensable components of the 3D content creation pipeline. The creative flexibility in modeling allows for generating captivating and innovative designs. At the same time, the technical accuracy in rendering ensures that these designs are transformed into realistic and visually stunning representations. Together, they empower artists, designers, and animators to bring their imaginative ideas to life in the world of digital art and design.
Similarities Between 3D Modeling and 3D Rendering
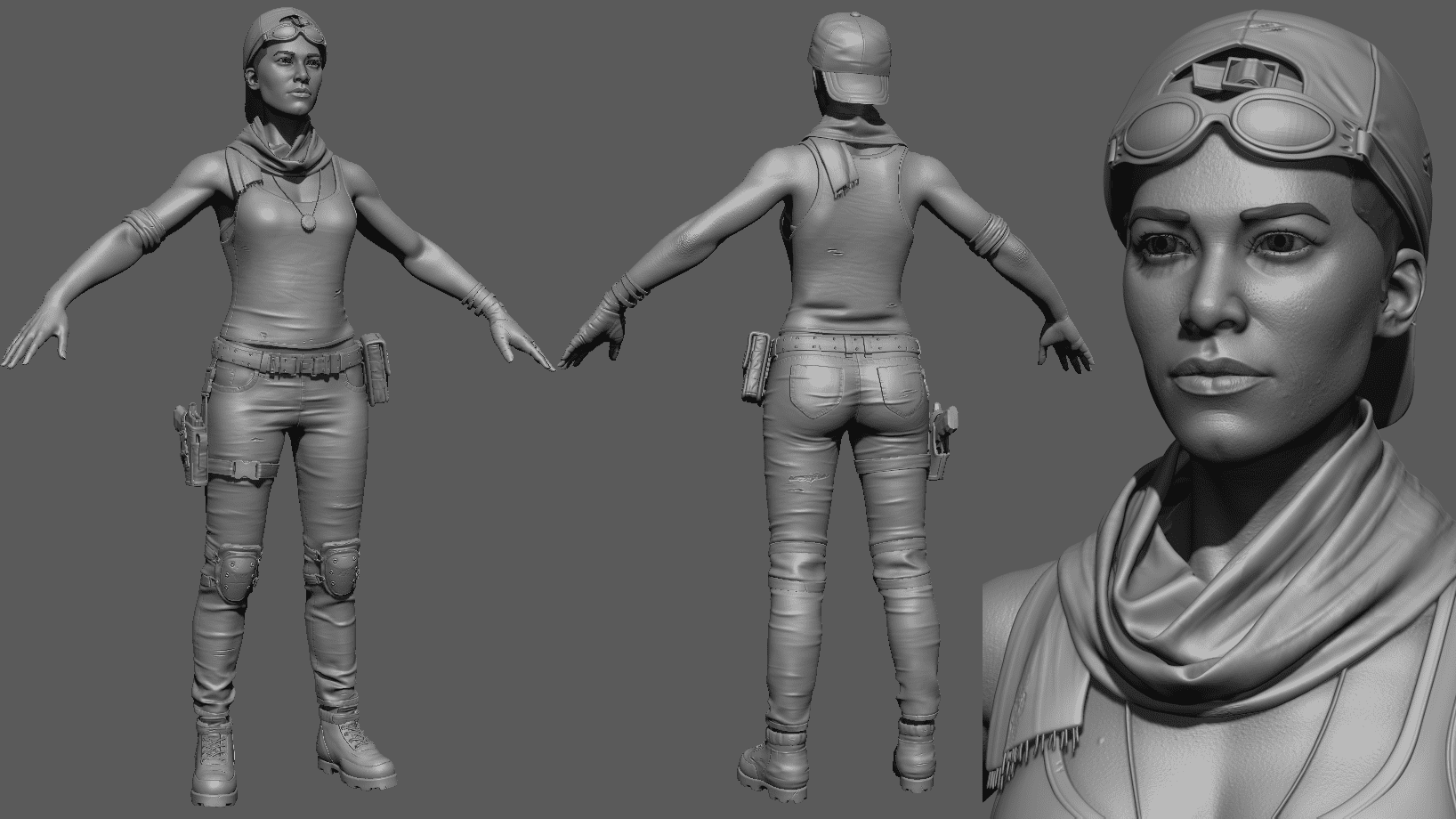
While 3D modeling and 3D rendering have notable differences, they also share some commonalities in their role within the 3D content creation process. Both techniques are essential to the broader 3D graphics pipeline, producing visually compelling and lifelike images, animations, and simulations.
One major similarity is that they both contribute to creating three-dimensional representations of objects and scenes. 3D modeling involves the construction of digital models using various tools and techniques, while 3D rendering transforms these models into realistic images or animations by simulating light, shadows, and other visual effects.
Additionally, both 3D modeling and 3D rendering rely heavily on specialized software designed to handle the complexities of working in three-dimensional space. These software packages offer various features and functionalities that enable artists and designers to effectively bring their creative visions to life.
Moreover, both techniques require a level of expertise and skill to achieve high-quality results. Skilled artists, animators, and designers with a deep understanding of form, composition, and lighting principles are crucial for successful 3D modeling and rendering processes.
In conclusion, while 3D modeling and 3D rendering serve distinct purposes in the world of digital art and design, their collaboration is indispensable in delivering captivating and visually immersive experiences to audiences across various industries, including video games, animation, architecture, product design, and more.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D modeling and 3D rendering are two indispensable pillars of modern digital art and design, each contributing unique elements to creating lifelike and immersive visual experiences. 3D modeling lays the foundation by constructing intricate digital models, while 3D rendering brings these models to life by simulating light, shadows, and other visual effects.
The interplay between these techniques empowers artists, designers, engineers, and developers to craft stunning visuals in various fields, from video games and animation to architecture and product design. As technology advances, the synergy between 3D modeling and rendering will continue to fuel creativity and innovation, shaping the future of digital content creation.



