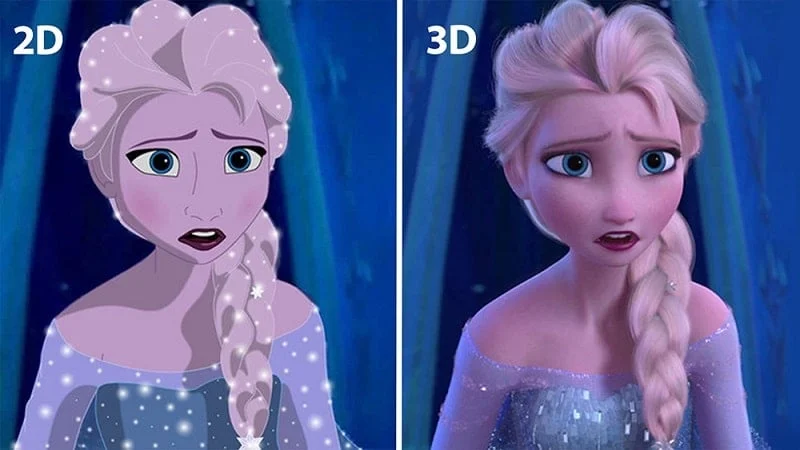
Animation has become an integral part of our entertainment landscape, captivating audiences with its ability to bring characters and stories to life. Two prominent techniques in the realm of animation are 2D animation vs 3D animation. Each technique offers its unique characteristics, visual appeal, and creative possibilities. In this article, we delve into the exciting world of 2D animation vs 3D animation, exploring their differences, advantages, disadvantages, historical significance, and applications in various fields.
From classic hand-drawn animations to cutting-edge computer-generated imagery, both 2D and 3D animation have made remarkable strides in capturing our imagination and pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling. Understanding the distinctions between these two techniques is crucial for aspiring animators, enthusiasts, and professionals in the field. So, let’s embark on this journey of discovery and unravel the magic behind 2D and 3D animation.
What is 2D Animation?
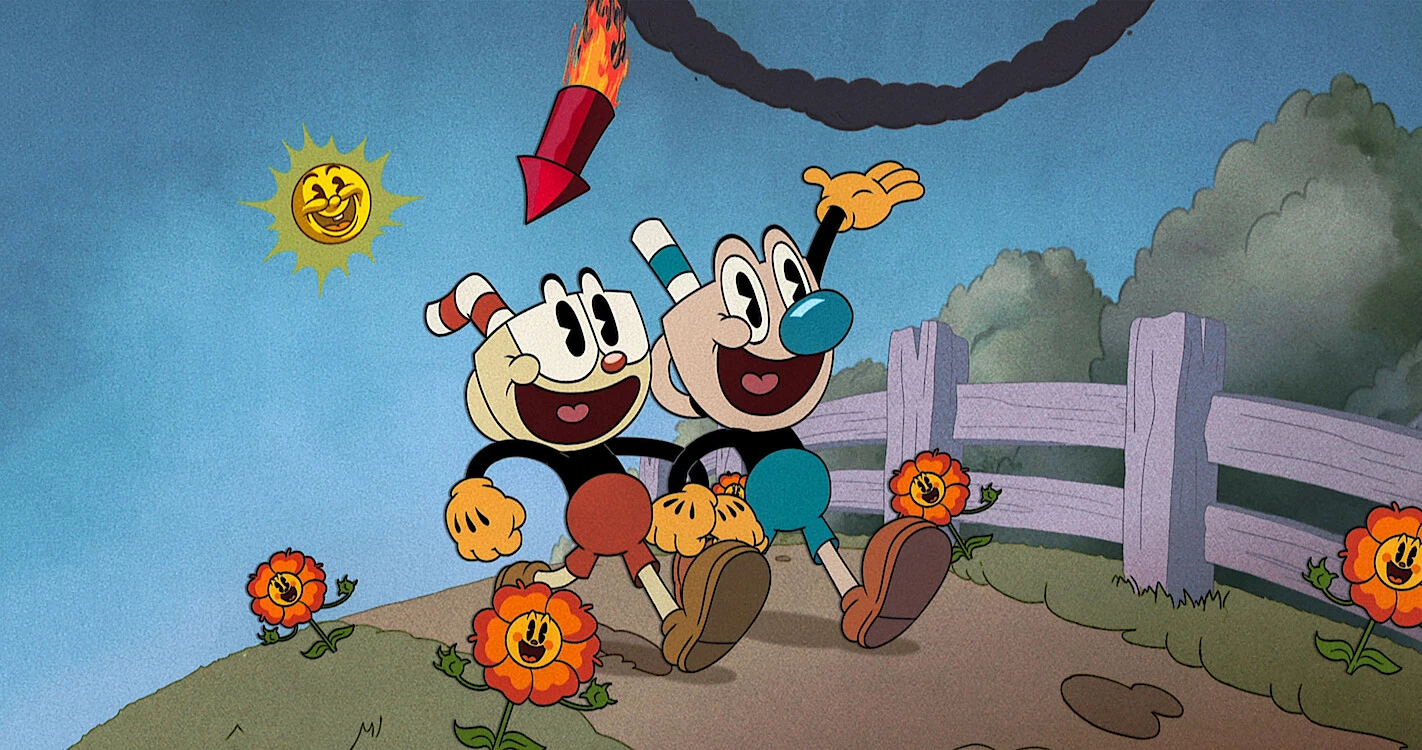


2D animation is a traditional animation technique that creates the illusion of movement through a series of hand-drawn or digitally created images. It involves creating individual frames that are played in rapid succession to give the impression of motion. In 2D animation, characters, backgrounds, and objects are typically drawn on a two-dimensional plane without depth. This classic animation style has been used for decades in films, television shows, advertisements, and video games to tell stories, convey emotions, and entertain audiences. With its distinctive charm and versatility, 2D animation continues to captivate viewers and remains a popular choice for artists and animators.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2D Animation

2D animation has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for certain types of projects and present challenges for others. Here, we explore some of the key advantages and disadvantages of 2D animation:
Advantages of 2D Animation
- Artistic Expression: 2D animation allows for artistic freedom and creativity. Artists can explore various styles, use vibrant colors, and create visually appealing characters and backgrounds. The hand-drawn or digitally painted nature of 2D animation offers a unique artistic touch.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to 3D animation, 2D animation is generally more affordable. It requires fewer resources and can be produced with lower production costs, making it a budget-friendly option for smaller projects or those with limited resources.
- Quicker Production: The process of 2D animation is typically faster than 3D animation. With the use of digital tools and software, artists can create and modify frames more efficiently, resulting in quicker production timelines.
- Classic Appeal: 2D animation has a nostalgic and classic charm that appeals to many viewers. It evokes a sense of familiarity and has a rich history in the world of animation, making it a preferred choice for certain genres or storytelling styles.
Disadvantages of 2D Animation
- Limited Depth and Realism: One of the main limitations of 2D animation is its lack of depth and realism compared to 3D animation. The flat nature of 2D characters’ art and backgrounds may not accurately represent the three-dimensional world, which can restrict certain visual effects and realistic movements.
- Technological Limitations: Traditional hand-drawn 2D animation requires significant skill and time commitment. While digital tools have simplified the process, achieving complex and detailed animations can still be challenging and time-consuming.
- Less Immersive Experience: The absence of depth and realistic textures in 2D animation may result in a less immersive experience for some viewers. The visual impact and sense of realism that can be achieved with 3D animation may be lacking in certain 2D projects.
- Limited Perspective: 2D animation often relies on a fixed perspective, which may limit camera angles and dynamic movements. This can make the animation feel more constrained compared to the freedom and versatility offered by 3D animation.
The History of 2D Hand Animation


2D hand animation, also known as traditional animation or cel animation, has a rich and fascinating history that spans over a century. It has played a pivotal role in shaping the world of animation and continues to inspire and influence contemporary animation techniques. Here, we delve into the key milestones and developments in the history of 2D hand animation:
- Early Innovations (Late 19th Century): The roots of 2D hand animation can be traced back to the late 19th century with the invention of devices like the zoetrope and flip book. These early mechanisms showcased sequential images that created the illusion of motion when spun or flipped rapidly.
- Emergence of Animation Studios (Early 20th Century): In the early 20th century, animation studios such as Walt Disney Studios and Warner Bros. began experimenting with animation techniques. The introduction of synchronized sound in the 1920s with Disney’s “Steamboat Willie” marked a significant milestone in the development of 2D animation.
- Golden Age of Animation (1930s-1950s): The Golden Age witnessed the rise of iconic characters like Mickey Mouse, Bugs Bunny, and Tom and Jerry. Studios like Disney, Warner Bros., and MGM produced many hand-drawn animated films, showcasing the artistry and storytelling capabilities of 2D animation.
- Introduction of Xerography (1960s): The introduction of xerography in the 1960s revolutionized the production process of 2D animation. This technique allowed animators to transfer pencil drawings directly onto cels, reducing the need for hand-inking and streamlining the production workflow.
- Digital Era (1980s-1990s): Digital technology brought significant advancements to 2D animation. Computer software like Adobe Flash (formerly Macromedia Flash) enabled animators to create vector-based animations more flexibly and efficiently.
- Renaissance of 2D Animation (2000s): Despite the rising popularity of 3D animation, the 2000s saw a resurgence of 2D animation, with films like “The Princess and the Frog” and “The Secret of Kells” garnering critical acclaim. Independent animators and studios also embraced the unique aesthetic and storytelling possibilities of 2D hand animation.
- Contemporary Landscape: Today, 2D hand animation continues to thrive in various forms, from feature films and television series to online content and video games. The availability of digital tools and software has made the creation of 2D animations more accessible, allowing artists to explore diverse styles and techniques.
What are the strengths of traditional animation?
Traditional animation, despite being difficult to make, has certain strengths that makes it hard to replace. Here are some of them:
- Artistic Expression: Traditional animation offers a unique platform for artistic expression, allowing animators to create visually stunning and emotionally resonant storytelling experiences. The hand-drawn nature of traditional animation allows for a high level of detail and craftsmanship, enabling animators to infuse their work with intricate character designs, expressive movement, and rich visual storytelling techniques.
- Timeless Aesthetic: Traditional animation possesses a timeless quality that transcends technological advancements and trends. The handcrafted nature of traditional animation imbues it with a sense of nostalgia and authenticity, evoking a connection to classic animated films and the golden age of animation. This timeless appeal resonates with audiences of all ages and backgrounds, ensuring the longevity and enduring popularity of traditional animation as an art form.
- Flexibility and Creativity: Traditional animation offers animators a high degree of flexibility and creative freedom in their artistic process. Unlike digital animation, which relies on predefined digital assets and rigging systems, traditional animation allows animators to sketch and animate characters and scenes by hand, enabling a more intuitive and organic approach to the animation process. This flexibility encourages experimentation and innovation, fostering a culture of creativity and artistic exploration within the animation industry.
Why is traditional animation important in modern day?
The importance of traditional animation In modern age can be attributed to 3 reasons:
- Artistic Heritage: Traditional animation serves as a cornerstone of the animation industry, embodying a rich artistic heritage and legacy that continues to inspire and influence contemporary animators and filmmakers. By preserving and celebrating the traditions of hand-drawn animation, modern-day animators pay homage to the pioneers and visionaries who paved the way for the art form’s evolution and innovation.
- Diverse Artistic Styles: Traditional animation offers a diverse range of artistic styles and techniques that complement and enhance modern animation practices. From classic Disney-style animation to experimental indie projects, traditional animation provides animators with a versatile toolkit for exploring different visual aesthetics and storytelling approaches. This diversity of styles adds depth and richness to the animation landscape, fostering a more vibrant and inclusive creative ecosystem.
- Human Touch: In an increasingly digital world, traditional animation provides a refreshing reminder of the human touch and craftsmanship that underpins the art form. The handcrafted nature of traditional animation imbues it with a sense of warmth, personality, and authenticity that resonates with audiences on a visceral level. This human element adds depth and emotional resonance to animated films and series, forging deeper connections between viewers and the stories they experience.
What is 3D Animation?
![]()
![]()
3D animation is a digital animation technique that brings characters, objects, and environments to life in a three-dimensional virtual space. Unlike traditional 2D animation, which is created by hand-drawing or manipulating flat images, 3D animation uses computer-generated graphics to simulate depth and movement. It involves the creation of 3D models, rigging them with a digital skeleton, animating their movements, applying lighting and textures, and rendering the final output. 3D animation is widely used in industries such as film, television, advertising, gaming, architecture, and education to create visually stunning and immersive experiences.
How 3D Animation Works
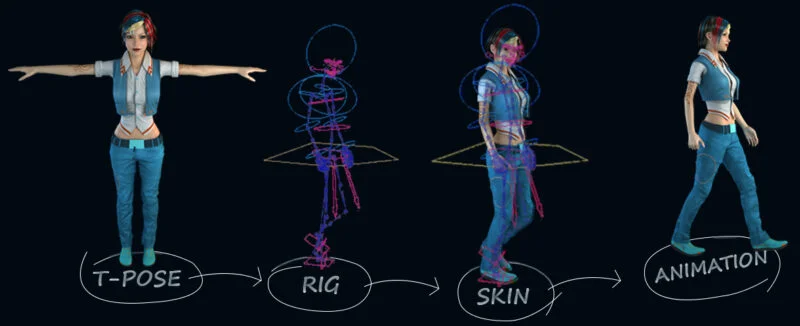

3D animation is a digital technique that creates lifelike and three-dimensional visuals using computer-generated imagery (CGI). It involves building virtual objects, characters, and environments in a digital 3D space. Artists use specialized software to model and shape the objects, add textures and colors, and define their movements. Through the manipulation of keyframes and animation curves, animators create realistic motions and poses. Lighting and camera setups are then applied to enhance the scene, and the final frames are rendered to produce the animation. 3D animation is widely used in various industries, including film, television, video games, and virtual reality, to create immersive and visually captivating experiences.
Evolution of 3D animation
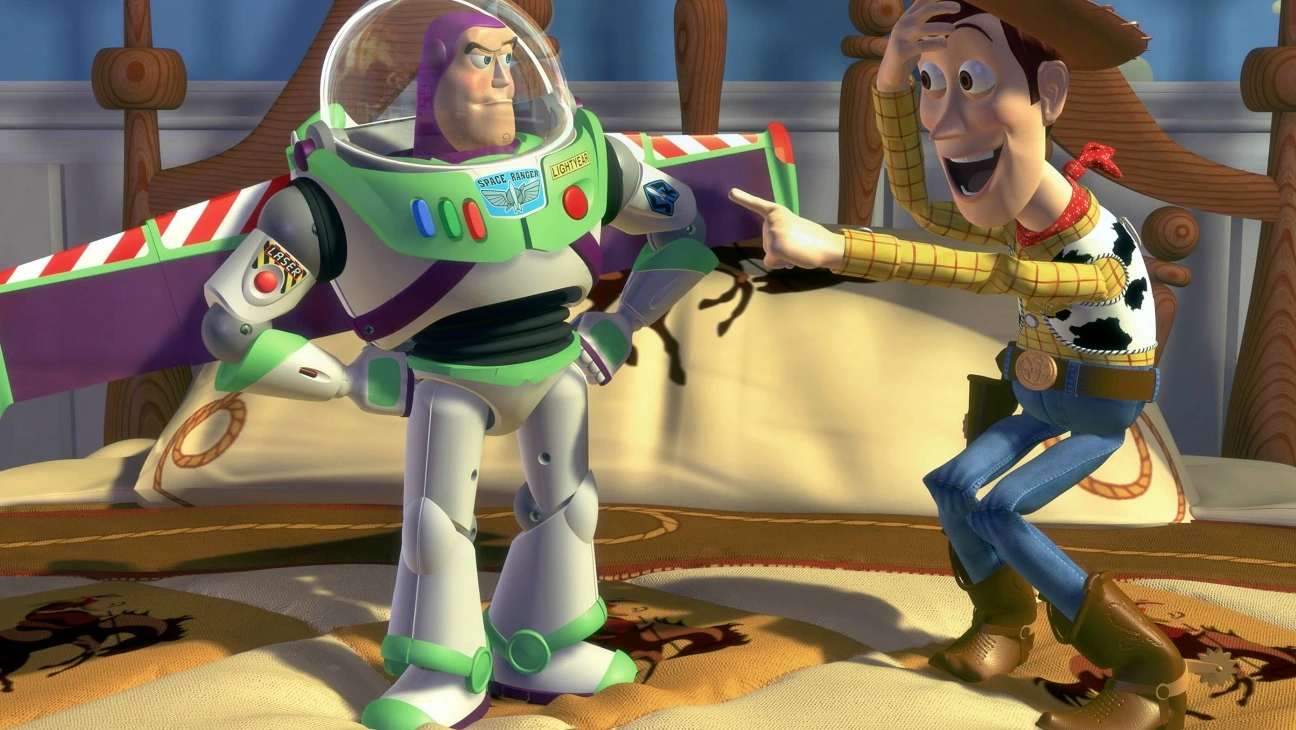


The evolution of 3D animation has been a fascinating journey marked by significant advancements in technology and artistic techniques. Over the years, the field has witnessed tremendous growth and innovation, transforming the way animations are created and presented.
In the early days, 3D animation was primarily limited to specialized studios and research institutions due to the high cost and technical complexity involved. However, with the advent of more accessible and powerful computer hardware and software, 3D animation became more feasible and widely adopted.
The 1980s saw the emergence of computer-generated imagery (CGI) in films, with notable examples such as “Tron” and “The Last Starfighter” showcasing the potential of 3D animation. The development of 3D modeling studio and rendering software, such as Autodesk’s 3ds Max and Pixar’s RenderMan, played a crucial role in advancing the field.
In the 1990s, the release of groundbreaking films like “Toy Story” and “Jurassic Park” propelled 3D animation into the mainstream. These films demonstrated the ability of 3D animation to create realistic and immersive worlds, captivating audiences worldwide.
As technology continued to evolve, so did the techniques and tools used in 3D animation. Motion capture systems became more sophisticated, allowing for more realistic character movements. The introduction of physics-based simulations enabled the creation of convincing natural phenomena like water, fire, and cloth.
In recent years, real-time rendering capabilities have revolutionized the industry. With powerful graphics cards and game engines like Unreal Engine and Unity, artists can now create high-quality 3D animations in real-time, providing more flexibility and interactivity.
The future of 3D animation looks promising, with ongoing advancements in areas such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence. These technologies open up new possibilities for immersive storytelling and interactive experiences.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Animation
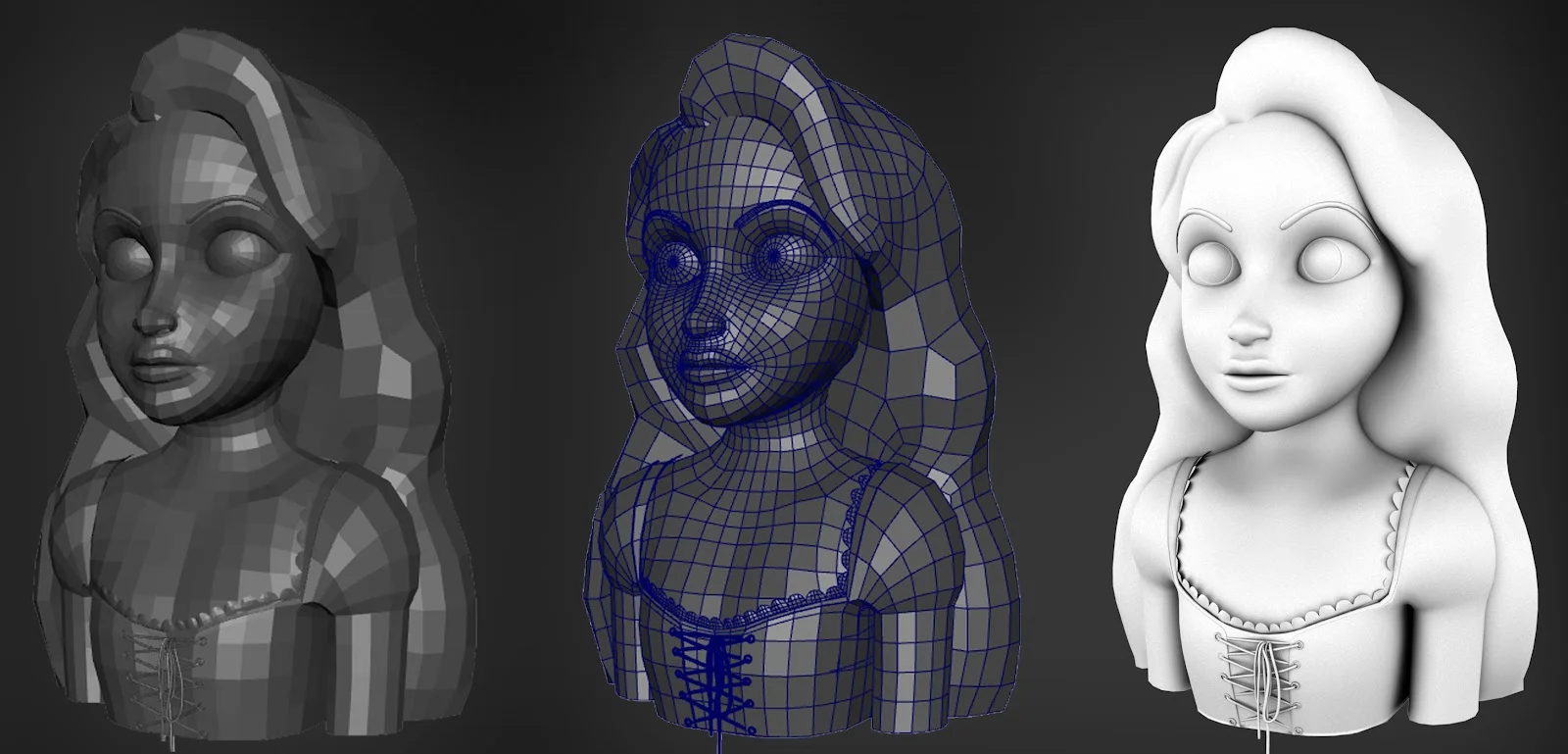

3D animation has revolutionized the world of visual storytelling and digital content creation. With its ability to create highly realistic and lifelike visuals, 3D animation has become a preferred choice for many industries, including film, gaming, advertising, and architectural visualization. However, along with its many advantages, there are also some inherent challenges and drawbacks to consider. Let’s go through some of them:
Advantages of 3D Animation
- Highly realistic and lifelike visuals
- Versatility and adaptability across various industries
- Precise control over movement and behavior
- Seamless integration with live-action footage or visual effects
- Enhanced viewer engagement and immersive storytelling
Disadvantages of 3D Animation
- Steep learning curve and complex software requirements
- Time-consuming rendering process for high-resolution scenes
- Costly investment in hardware, software, and skilled professionals
- Potential reliance on a team of specialized artists for high-quality production
2D Animation vs 3DAnimation – Major Differences


When it comes to animation, two prominent techniques dominate the industry: 2D animation vs 3D animation. While both approaches bring characters and stories to life, they differ significantly in their execution and visual style. We are going to delve into the major differences between 2D animation vs 3D animation, exploring their distinct characteristics, applications, and creative possibilities. By understanding these differences, you can decide which animation style best suits your project and effectively conveys your vision to your audience.
Field of Application
2D Animation:
- Traditional 2D animation has been widely used in the film and television industry for decades.
- It is commonly seen in cartoons, animated series, advertisements, and explainer videos.
- 2D animation is also popular in game development stages, particularly in the creation of retro-style or pixel art games.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation has a broad range of applications in various industries, including film, television, gaming, architecture, engineering, and advertising.
- It is extensively used in the production of animated movies, visual effects in live-action films, video games, architectural visualizations, and product simulations.
- 3D animation allows for highly realistic and immersive experiences, making it suitable for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications.
Tools
2D Animation:
- Traditional 2D animation often relies on hand-drawn techniques, where artists use pen and paper or digital drawing tablets.
- Digital software such as Adobe Animate, Toon Boom Harmony, and TVPaint are commonly used for creating and editing 2D animations.
- These tools offer a variety of features for drawing, coloring, frame sequencing, and adding effects to bring characters and scenes to life.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation involves the use of specialized software that allows artists to model, rig, animate, and render 3D objects and characters.
- Popular 3D animation software includes Autodesk Maya, Blender, Cinema 4D, and 3ds Max.
- These tools offer powerful capabilities for modeling complex 3D geometries, applying textures and materials, setting up character skeletons, and creating lifelike animations.
Complexity
2D Animation:
- 2D animation typically has a simpler visual style, with flat, two-dimensional characters and backgrounds.
- It involves the creation of individual frames or key poses that are then sequenced to produce the illusion of motion.
- The complexity of 2D animation can vary depending on the level of detail, movement, and special effects required in the project.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation involves working with three-dimensional objects and environments, requiring a deeper understanding of 3D modeling, texturing, lighting, and animation principles.
- It often involves the creation of complex character rigs, realistic physics simulations, and intricate camera movements.
- The level of complexity in 3D animation can vary significantly based on the project’s requirements, ranging from simple object animations to highly detailed character performances and visual effects.
Budget
2D Animation:
- Traditional 2D animation can be relatively cost-effective, especially for simpler productions or shorter projects.
- The cost largely depends on factors such as the length of the animation, the level of detail, the number of frames, and the complexity of the visuals.
- With the availability of digital tools, 2D animation has become more accessible and affordable for independent animators and small studios.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation can be more resource-intensive and costly compared to 2D animation due to the additional technical requirements and the need for specialized software and hardware.
- The complexity of 3D modeling, texturing, rigging, and rendering processes can contribute to higher production costs.
- Larger budgets are often required for high-quality 3D animation projects, particularly those involving detailed character animations, realistic simulations, and visual effects.
Resources
2D Animation:
- 2D animation relies heavily on the skills and creativity of the artists.
- Artists need proficiency in drawing, character design, storytelling, and animation principles to create compelling 2D animations.
- Access to drawing tools, animation software, and reference materials such as storyboards and concept art studios is essential.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation requires a combination of artistic skills and technical knowledge.
- Artists need to learn 3D modeling, texturing, rigging, animation techniques, and rendering processes.
- Access to specialized software, powerful computers, and online resources such as tutorials, forums, and asset libraries can greatly support the 3D animation workflow.
Time
2D Animation:
- 2D animation can be time-consuming, especially when it involves hand-drawn techniques or frame-by-frame animation.
- The time required depends on factors such as the length of the animation, the level of detail, the complexity of movements, and the number of frames.
- Efficient planning, storyboarding, and effective use of animation software can help streamline the production process.
3D Animation:
- 3D animation often requires more time compared to 2D animation due to the additional steps involved in modeling, rigging, texturing, and rendering.
- The complexity of the project, the level of detail in the 3D models, the intricacy of animations, and the rendering times can significantly impact the overall production timeline.
- Collaborative workflows, project management tools, and efficient rendering techniques can help optimize the time required for 3D animation projects.
Best 2D Animation Software
Several software options are well-regarded for 2D animation:
- Adobe Animate: Formerly known as Flash, Adobe Animate is a professional tool for creating interactive animations and cartoons.
- Toon Boom Harmony: A versatile software used by many studios and independent animators for 2D animation.
- TVPaint Animation: Known for its traditional hand-drawn animation capabilities, TVPaint is favored by artists looking for a classic feel.
- Moho (formerly Anime Studio): Moho is a user-friendly 2D animation software that offers bone-rigging capabilities for character animation.
- Pencil2D: An open-source and free 2D animation software suitable for beginners and hobbyists.
Best 3D Animation Software
For 3D animation, several powerful software options include:
- Autodesk Maya: A versatile and industry-standard software used for 3D animation, modeling, and rendering.
- Blender: An open-source 3D creation suite that is powerful and free, making it popular among independent creators.
- Cinema 4D: Known for its user-friendly interface and powerful 3D animation capabilities, Cinema 4D is used in various industries, including motion graphics and visual effects.
- Houdini: Particularly acclaimed for its procedural animation and effects capabilities, Houdini is favored for complex simulations and VFX.
- 3ds Max: Autodesk’s 3ds Max is used for game development, architectural visualization, and character animation.
Future of 2D vs. 3D Animation
The future of 2D and 3D animation is a complex and multifaceted landscape:
2D Animation:
While 2D animation maintains its charm and appeal, its future is increasingly intertwined with digital technology. With the advent of powerful software tools, 2D animation is experiencing a resurgence, especially in independent and web-based content. There is a growing interest in mixing 2D and 3D elements, offering unique visual experiences.
3D Animation:
3D animation is expected to continue dominating industries like gaming, film, architecture, and advertising. Technological advancements, such as real-time rendering and virtual reality, will further enhance its capabilities. The democratization of 3D animation tools and the growth of indie game development are poised to fuel innovation in the 3D animation sector.
The future of both forms of animation is interconnected, as artists increasingly explore hybrid approaches that blend the strengths of 2D and 3D techniques. Whether it’s the evocative storytelling of 2D animation or the immersive worlds of 3D animation, both have their place in the ever-evolving world of visual media, offering rich and diverse storytelling opportunities.
Conclusion
2D animation vs 3D animation offer distinct approaches to bringing visuals to life in the world of animation and beyond. 2D animation is characterized by its traditional, hand-drawn techniques and simpler visual style, making it well-suited for cartoons, advertisements, and retro-style games. On the other hand, 3D animation utilizes three-dimensional objects and environments, allowing for highly realistic and immersive experiences in film, television, gaming, architecture, and more.
Each form of animation comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. 2D animation offers a rich history, ease of entry, and cost-effectiveness, while 3D animation provides unparalleled realism, complexity, and versatility. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the project, including its field of application, the available tools and resources, the desired level of complexity, budget constraints, and time considerations.
Ultimately, both 2D animation vs 3D animation have their place in the world of animation, offering unique artistic and storytelling possibilities. As technology advances, animators and artists have the opportunity to explore new techniques and push the boundaries of visual storytelling, creating captivating experiences for audiences worldwide.


