In the creative realm of digital art, two distinct approaches reign supreme—vector art vs. raster art. Each represents a unique philosophy of creation, bringing its own set of tools, techniques, and possibilities to the canvas. In this exploration, we delve into the worlds of vector art vs. raster art, unraveling their essence, applications, and the creative strengths they offer. Whether you’re a seasoned graphic designer, a digital illustrator, or simply a curious enthusiast, this journey aims to illuminate the differences between these two artistic realms and guide you in choosing the most suitable medium for your creative aspirations. From pixel-perfect raster compositions to the limitless scalability of vectors, join us in understanding the artistic dichotomy of vector art vs. raster art.
What is Raster Art?


Raster art, also known as bitmap or pixel-based art, is a digital art form that is created by arranging individual colored pixels on a grid to form an image. Each pixel is a tiny, discrete element, and the combined arrangement of these pixels creates the visual composition.
Raster images are resolution-dependent, meaning that their quality is determined by the number of pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). Higher resolutions result in sharper and more detailed images, while lower resolutions may appear pixelated.
What is Raster Art Used for?
Raster art finds widespread use in various creative disciplines, including digital illustration, photography, graphic design, and web design. It is particularly suitable for capturing intricate details, nuanced shading, and complex textures, making it ideal for projects where visual realism and fine-grained detail are essential.
Raster art is commonly employed in tasks such as photo editing, image manipulation, digital painting, and creating rich, textured graphics.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Raster Art

Advantages
- Detail and Realism: Raster art excels in capturing intricate details and realistic textures, making it ideal for lifelike illustrations and photo editing.
- Flexibility: Artists have precise control over individual pixels, allowing for complex shading and blending techniques.
- Widespread Compatibility: Raster files (e.g., JPEG, PNG) are universally supported and can be easily shared and viewed on various devices and platforms.
Disadvantages
- Resolution Limitation: Raster images are resolution-dependent, which means they may lose quality if scaled up significantly.
- File Size: High-resolution raster images can result in large file sizes, which can be cumbersome for storage and online sharing.
- Limited Scalability: Enlarging raster images often leads to pixelation and loss of quality.
What Software is Used to Create Raster Art?


A plethora of software options cater to raster art creation, each offering a unique set of tools and features. Some popular choices include Adobe Photoshop, Corel Painter, GIMP (GNU Image Manipulation Program), Krita, and Clip Studio Paint. These programs provide a wide range of brushes, filters, and editing capabilities to empower artists in crafting stunning raster artworks.
What is Vector Art?


Vector art is a digital art form created using mathematical equations to define shapes and lines. Unlike raster art, which relies on pixels, vector art employs a network of precise geometric objects such as points, lines, curves, and polygons to construct images.
These mathematical representations ensure that vector images remain crisp and sharp at any scale, as they are resolution-independent. Vector art is characterized by its ability to maintain clarity and quality when enlarged or scaled down, making it an ideal choice for projects that require scalability and precision.
What is Vector Art Used for?
Vector art finds versatile applications across various creative domains. It is commonly used in graphic design, logo creation, typography, iconography, illustration, and print media. Vector images are especially suitable for projects that require sharp, clean lines and well-defined shapes, such as company logos, business cards, signage, and infographics. They are also frequently used in animation, as vector objects can be easily manipulated and animated with smooth transitions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vector Art

Advantages:
- Scalability: Vector images can be resized indefinitely without loss of quality, making them perfect for projects that require various output sizes.
- Clarity: Vector art is known for its sharp and precise lines, ideal for producing clear and well-defined graphics.
- Small File Sizes: Vector files are typically small in size, making them easy to share and store.
- Editable: Vector art remains fully editable, allowing for easy modifications and updates to the artwork.
Disadvantages:
- Complex Detailing: Vector art may not be as well-suited for capturing intricate textures and fine shading as raster art.
- Learning Curve: Creating vector art requires familiarity with vector editing software and a different skill set compared to traditional drawing or painting.
- Not Ideal for Realism: While vector art excels in crisp, stylized visuals, it may not be the best choice for highly realistic illustrations or photographs.
What Software is Used to Create Vector Art?


A variety of vector graphics software options are available to cater to the creation of vector art. Some of the most popular choices include Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, Inkscape (an open-source option), Affinity Designer, and Vectr.
These programs provide a comprehensive suite of tools for drawing, editing, and manipulating vector shapes, allowing artists and designers to craft precise and scalable vector artworks for a wide range of creative projects.
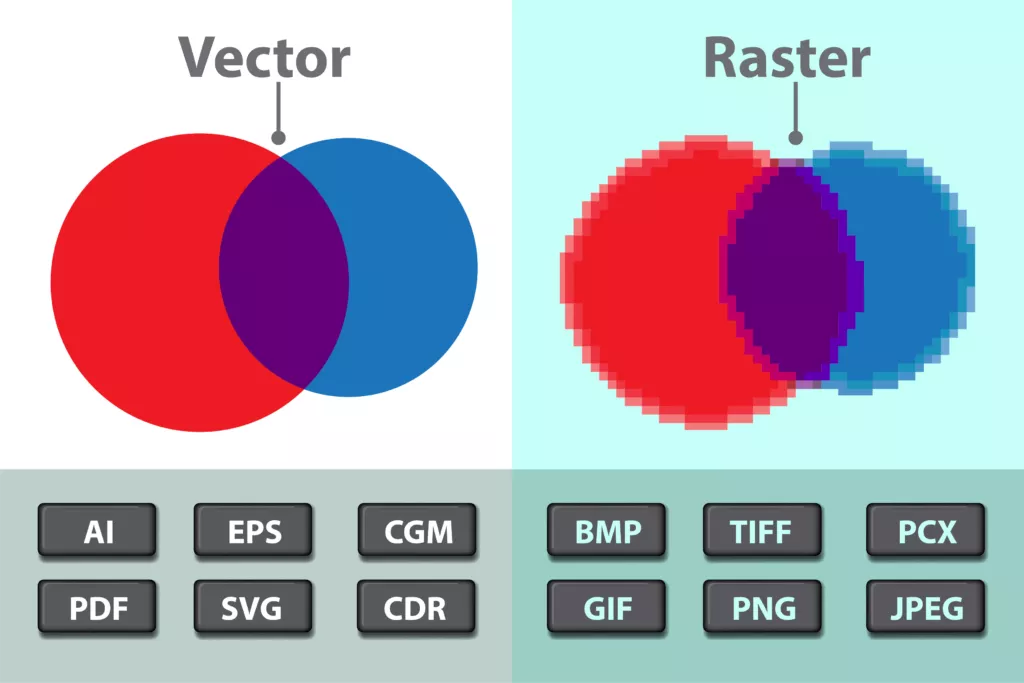
Difference Between Vector Art vs. Raster Art
The primary distinction between vector art vs. raster art lies in their fundamental composition and use cases. Vector art is constructed from mathematical equations, utilizing precise geometric shapes to define graphics, making it inherently resolution-independent and ideal for projects requiring scalability and precision. In contrast, raster art relies on a grid of pixels, excelling in capturing intricate details and realistic textures but being resolution-dependent.
Vector art is favored for tasks like logo design, typography, and graphics, where clarity and scalability are paramount. Raster art shines in digital painting, photography, and projects demanding intricate textures. The choice between the two depends on the specific project requirements, with vector art offering clarity and scalability and raster art providing intricate, realistic details.
What Game Artists Choose | Vector Art vs. Raster Art
Game artists often face a crucial decision when creating game assets. The choice between vector art vs. raster art hinges on the game’s style and requirements. Vector art is favored for games with stylized graphics, crisp visuals, and scalability needs, like mobile games or platformers. It ensures assets remain sharp across different screen sizes.
Raster art, on the other hand, shines in games aiming for photorealism or rich textures, such as first-person shooters or open-world RPGs. It allows for intricate detailing and realism. In some cases, a hybrid approach is adopted, combining vector elements for UI and icons with raster art for in-game textures and character design, offering the best of both worlds.
Final Thoughts
In the realm of digital artistry, the choice between vector art vs. raster art isn’t just a matter of preference but a strategic decision driven by the project’s unique demands. Vector art offers clarity, precision, and limitless scalability, making it the go-to choice for logos, icons, and graphics that need to shine at any size. Raster art, on the other hand, excels in capturing nuanced textures and photorealistic details, making it indispensable for digital painting and photography.
The artistry of game design often calls for a thoughtful blend of both, where vector art ensures crisp UI elements and icons, while raster art breathes life into in-game assets and textures. The magic of digital artistry lies in mastering these diverse tools to bring imagination to life on the digital canvas.