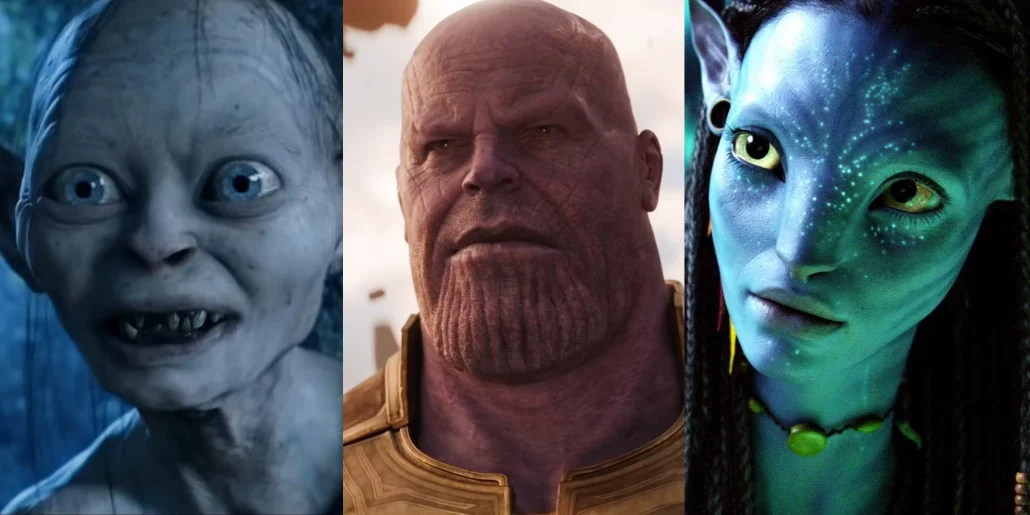
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on CGI and 3D animation! In today’s digital age, computer-generated imagery (CGI) and 3D animation have become integral parts of various industries, from film and television to gaming and advertising. Whether you’re a fan of visually stunning movies or an aspiring animator, understanding the fundamentals and applications of these concepts is essential.In this article, we will delve into the world of CGI and 3D animation, exploring their definitions, differences, and common uses. We’ll uncover the power and versatility of these technologies and shed light on their unique advantages. By the end, you’ll understand how they contribute to creating immersive and visually captivating experiences.
What is CGI?
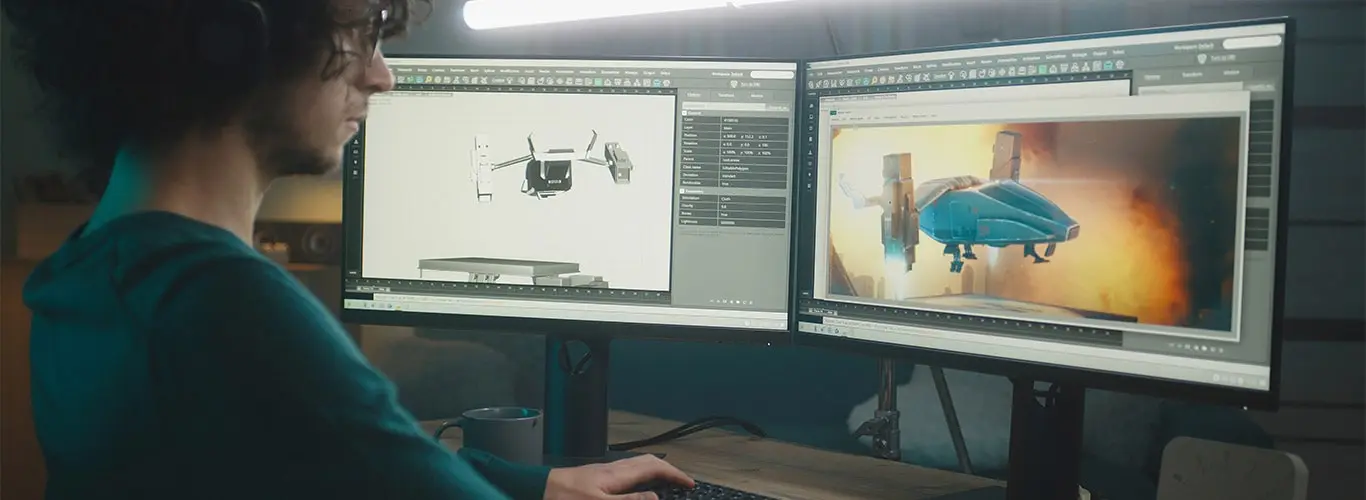

CGI, or computer-generated imagery, refers to creating and manipulating visual content using computer software and technology. It involves generating lifelike images, animations, and special effects that appear realistic and are typically difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional methods. CGI has revolutionized how visuals are created and have become a crucial component in various industries, including film, television, advertising, video games, and architectural visualization.
With CGI, artists and animators can design and construct virtual environments, characters, objects, and visual elements seamlessly blending with real-world footage or stand alone as entirely computer-generated scenes. CGI artists can manipulate lighting, textures, camera angles, and physics by harnessing powerful software and techniques to create stunning and immersive visual experiences.
CGI enhances visual storytelling, creates realistic visual effects, simulates environments or objects, and brings fantastical creatures and worlds to life. It has become an indispensable tool for filmmakers, allowing them to create breathtaking scenes, breathtakingly realistic characters, and captivating visual narratives. From blockbuster movies to TV shows, commercials, and even virtual reality experiences, CGI plays a pivotal role in shaping our visual landscape and pushing the boundaries of artistic expression.
How is CGI used in animation?
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the field of animation by providing artists with powerful tools to create stunning visuals and realistic environments. In animation, CGI is used to generate digital imagery and special effects that enhance the visual appeal and realism of animated scenes. CGI allows animators to create complex characters, dynamic environments, and intricate visual effects that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional animation techniques alone. By leveraging advanced software and rendering technologies, animators can manipulate digital models, simulate physics-based interactions, and generate lifelike animations with unprecedented detail and precision.
The Primary Types of CGI Animation
There are several primary types of CGI animation, each characterized by its unique approach to creating digital imagery and special effects:
- 3D Animation: Also known as computer-generated animation, 3D animation involves creating digital models and environments using specialized software and then animating these elements to produce lifelike movement and interactions. 3D animation is widely used in feature films, television shows, video games, and advertisements due to its versatility and ability to create highly realistic visuals.
- Visual Effects (VFX): CGI is often used to create visual effects that enhance the realism and spectacle of animated scenes. VFX techniques include simulating explosions, fire, smoke, water, and other natural phenomena, as well as creating fantastical creatures, magical spells, and futuristic technology. VFX artists use a combination of modeling, texturing, animation, and compositing techniques to seamlessly integrate CGI elements into live-action footage or animated sequences.
- Motion Graphics: CGI is also used to create motion graphics, which are animated graphics that convey information, narratives, or visual concepts in a dynamic and engaging manner. Motion graphics are commonly used in title sequences, logo animations, explainer videos, and user interfaces to add visual interest and convey complex information in a concise and accessible format. CGI allows motion graphic designers to create fluid animations, dynamic transitions, and eye-catching visual effects that captivate viewers and enhance the overall viewing experience.
What Is CGI Animation?
CGI animation, or computer-generated animation, refers to the process of creating animated sequences using digital models, environments, and visual effects generated by computer software. Unlike traditional animation techniques, which rely on hand-drawn animation or stop-motion animation methods, CGI animation involves manipulating digital assets within a virtual environment to produce lifelike movement, textures, and lighting effects. CGI animation is widely used in the entertainment industry to create feature films, television shows, video games, and advertisements, as well as in scientific visualization, architectural rendering, and virtual reality applications. With its ability to create highly realistic and immersive visuals, CGI animation has become an indispensable tool for animators, filmmakers, and visual effects artists seeking to push the boundaries of creativity and storytelling.
What Is 3D Animation?
3D animation is a technique that involves creating and animating three-dimensional digital objects or characters within a virtual environment. Unlike traditional 2D animation that works with flat, two-dimensional images, 3D animation adds depth, realism, and an extra dimension to the animation process. It brings virtual objects to life by manipulating their shape, movement, texture, and lighting.
In 3D animation, artists use specialized software to build virtual models, often referred to as wireframes, which serve as the foundation for the animation. These models can represent various objects, from simple geometric shapes to complex characters and environments. Artists then apply textures, colors, and surface properties to these models to make them appear realistic or stylized, depending on the desired aesthetic.
The animation process involves creating a series of keyframes or poses that define the position, orientation, and other attributes of the 3D objects at specific points in time. These keyframes are then interpolated to generate smooth and fluid movements between them, resulting in lifelike animation. Additionally, 3D animation allows for applying physics-based simulations, such as gravity, collision detection, and particle effects, to further enhance realism and dynamics in the animation.
3D animation finds applications in various industries, including film, television, video games, advertising, architectural visualization, and product design. It offers many creative possibilities, allowing artists to bring imaginary worlds, characters, and objects to life with stunning detail and visual fidelity. Whether it’s crafting compelling visual effects, character animation, product demonstrations, or architectural walkthroughs, 3D animation adds depth and realism to the digital realm, captivating audiences and pushing the boundaries of visual storytelling.
The Difference Between 3D Animation and 2D Animation
The difference between 3D and 2D animation lies in how the images are created and presented. While both techniques involve creating animated visuals, they differ in their visual style, depth, and the tools used for their creation.
2D animation, also known as traditional or hand-drawn animation, is the oldest form of animation. It involves creating a sequence of images or frames that are displayed in rapid succession to create the illusion of movement. In 2D animation, the characters, objects, and backgrounds are typically created and animated on a flat plane, with only width and height considered. Artists draw each frame by hand or use digital tools to create the illustrations. The resulting animation looks more stylized and often less realistic than 3D animation.
On the other hand, 3D animation adds an extra dimension of depth to the visuals. It involves creating three-dimensional models of objects or characters and animating them within a virtual environment. The models are built using specialized software and consist of wireframes that define the shape and structure of the objects. Artists then apply textures, colors, and other surface properties to make the models appear realistic or stylized. The animation process involves manipulating the models’ positions, orientations, and other attributes over time to create movement.
The key difference between 3D animation and 2D animation is the level of visual depth and realism. While 2D animation focuses on creating movement within a two-dimensional space, 3D animation allows for creating a fully 3d environment design and characters. This depth adds a sense of realism and immersion to the animation, making it more visually engaging and dynamic.
Another difference is the tools and software used in each technique. 2D animation can be created using traditional hand-drawn techniques or digital software such as Adobe Animate or Toon Boom Harmony. 3D animation, on the other hand, requires specialized software such as Autodesk Maya and Blender or Cinema 4D, which are designed specifically for creating and animating three-dimensional models.
Both 2D and 3D animation have their unique advantages and applications. 2D animation is often used in traditional hand-drawn animation, motion graphics, and certain types of games. It has a distinct visual style and is well-suited for projects that require a more artistic or stylized approach. 3D animation, on the other hand, is commonly used in films, television shows, video games, architectural visualization, and product design. Its ability to create realistic and immersive visuals makes it a popular choice for projects that require a high level of detail and realism.
In summary, the main differences between 3D animation and 2D animation are the level of visual depth and realism, the tools and software used, and the overall visual style. Both techniques have their strengths and applications, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements and artistic vision of the project at hand.
The Difference Between CGI and 3D Animation
The terms CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) and 3D animation are often used interchangeably, but there is a subtle distinction between the two.
CGI refers to using computer graphics to create visual elements in films, television shows, advertisements, and other media. It encompasses various techniques and applications, including 3D animation, visual effects, virtual environments, and digital compositing. CGI uses powerful software and hardware systems to create and manipulate digital assets, such as models, textures, lighting, and special effects.
On the other hand, 3D animation specifically refers to the process of creating moving images in a three-dimensional space. It involves using computer-generated 3D modeling studios and environments, which are animated by manipulating their positions, orientations, and attributes over time. 3D animation can be a subset of CGI, as it falls under the broader umbrella of computer-generated imagery.
In simpler terms, CGI is a broader term that encompasses various digital techniques used to create visuals, while 3D animation specifically focuses on the creation of animated content within a three-dimensional space.
CGI can include not only 3D animation but also other elements like digital effects, motion graphics, and virtual environments. It is widely used in the entertainment industry to enhance visual storytelling and create realistic or fantastical worlds that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional practical effects alone.
On the other hand, 3D animation is a specific subset of CGI that deals with animating three-dimensional objects, characters, and environments. It involves the process of modeling, texturing, rigging, and animating digital assets to create the illusion of movement and bring them to life.
In summary, the difference between CGI and 3D animation lies in their scope and focus. CGI encompasses a broader range of computer-generated imagery techniques, while 3D animation specifically deals with creating animated content within a three-dimensional space. Both play crucial roles in producing visually stunning and immersive media experiences.
What Are CGI and 3D Animation Used For?
CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) and 3D animation have become integral parts of various industries and have a wide range of applications. Here are some common uses for CGI and 3D animation:
- Film and Television: CGI and 3D animation have revolutionized the film and television industry. They are used to create realistic or fantastical visual effects, animated characters, and immersive environments that bring stories to life and enhance the viewer’s experience.
- Advertising and Marketing: CGI and 3D animation are extensively used in commercials, product visualizations, and digital marketing campaigns. They allow advertisers to showcase products and concepts visually, compellingly, and engagingly. They help create eye-catching visuals, demonstrate product functionality, and bring ideas to life in a memorable manner.
- Video Games: The gaming industry heavily relies on CGI and 3D animation to create interactive and visually stunning game worlds. 3D animation brings characters, creatures, and environments to life, while CGI renders realistic graphics, special effects, and cinematic sequences. These technologies play a crucial role in providing immersive gaming experiences.
- Architectural Visualization: CGI and 3D animation are utilized in architectural design and visualization. They enable architects and designers to create virtual walkthroughs, realistic renderings, and interactive presentations of buildings and interior spaces. This allows clients and stakeholders to visualize designs before construction and make informed decisions.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): CGI and 3D animation create immersive experiences in VR and AR applications. They are used to develop realistic virtual environments, interactive simulations, and lifelike avatars. They contribute to the sense of presence and enhance the realism of these virtual worlds.
- Medical and Scientific Visualization: CGI and 3D animation are vital in medical and scientific fields. They are used to visualize complex biological processes, anatomy, medical procedures, and scientific concepts. These computer-generated animations help in education, research, and communication within these fields by creating detailed and accurate visual representations.
- Education and Training: CGI and 3D animation are employed in educational settings to create engaging and interactive learning materials. They can simulate scientific experiments, historical events, and complex concepts, making learning more accessible and captivating.
The applications of CGI and 3D animation are diverse and constantly expanding. They have become indispensable tools in various industries, enabling the creation of visually compelling content, enhancing communication, and pushing the boundaries of creativity and innovation.
The Advantages of CGI and 3D Animation


CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) and 3D animation offer several advantages that have made them indispensable in various industries. Here are some key advantages of using CGI and 3D animation:
- Realism and Visual Appeal: CGI and 3D animation can create highly realistic and visually stunning graphics, characters, and environments. The detail, texture, and lighting level can be meticulously crafted to achieve a lifelike appearance. This realism enhances the overall quality and immersion of the final product, whether it’s a movie, video game, or architectural visualization.
- Creative Freedom: CGI and 3D animation provide artists and designers immense creative freedom. They allow for creation of imaginative and fantastical worlds, characters, and visual effects that may not be feasible in the real world. Artists can bring their ideas to life without the constraints of practical limitations, enabling unique and compelling storytelling.
- Flexibility and Control: With CGI and 3D animation, artists have precise control over every aspect of the visual elements. They can easily manipulate and modify objects, camera angles, lighting, and textures, allowing quick iterations and adjustments. This flexibility makes achieving the desired look and feel easier, saving time and resources compared to traditional methods.
- Cost Efficiency: While the initial investment in CGI and 3D animation software and hardware can be significant, they often prove cost-effective in the long run. Once the assets are created, they can be reused and repurposed for different projects, reducing the need for physical sets, props, or reshoots. Additionally, they allow for streamlined production workflows, saving time and reducing expenses associated with practical effects.
- Improved Workflow and Collaboration: CGI and 3D animation software provide powerful tools for project management, asset organization, and collaboration. Artists and teams can work concurrently on different aspects of a project, easily sharing and integrating their work. This streamlined workflow enhances productivity, simplifies revisions, and facilitates seamless collaboration between artists, designers, and other stakeholders.
- Experimental and Exploratory Possibilities: CGI and 3D animation enable artists and designers to experiment with different styles, techniques, and visual approaches. They can explore unconventional aesthetics, push the boundaries of reality, and create unique visual experiences. This experimental nature opens up new creative possibilities and allows fresh and innovative content to be developed.
- Accessibility and Distribution: CGI and 3D animation can be easily distributed and accessed across various platforms and devices. Whether it’s a movie, video game, virtual reality experience, or online advertisement, the digital nature of computer-generated animations allows for widespread distribution and easy consumption by audiences worldwide.
The advantages of CGI and 3D animation have transformed how visual content is created, enhancing various media’s quality, scope, and impact. Their versatility, realism, and creative potential continue to push the boundaries.
What is 3D CGI?


In the realm of visual art and entertainment, 3D CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) stands as a technological wonder that has transformed how we perceive and experience images, animations, and movies. This revolutionary technique involves the creation, manipulation, and animation of digital objects and environments through the prowess of computer algorithms. It has not only paved the way for breathtaking visual spectacles but has also redefined the way we bring imagination to life.
Are 3D models CGI?
To grasp the concept of 3D CGI, it’s essential to clarify the distinction between 3D models and CGI. While closely related, they are not synonymous. A 3D model refers to a digital representation of an object or character in three dimensions, often created using specialized software. These models serve as the foundation upon which CGI is built. Computer-Generated Imagery, on the other hand, encompasses a broader spectrum, incorporating the manipulation, rendering, and animation of these 3D models to create realistic, dynamic visuals.
Is Avatar a CGI movie?
![]()
![]()
The film “Avatar,” directed by James Cameron, stands as a prime example of the awe-inspiring capabilities of CGI. Released in 2009, the movie utilized cutting-edge technology to craft an immersive and visually striking world on the fictional moon of Pandora. The film’s landscapes, creatures, and characters were predominantly computer-generated seamlessly integrated into live-action footage. While “Avatar” features a significant amount of CGI, it’s important to note that CGI does not solely encompass 3D models. The term also encompasses digital effects, enhancements, and animations that enhance the overall visual experience.
Best CGI Software For Beginners in 2023
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) has become an integral part of various industries, from animation and visual effects in films to architectural visualization and video game development. As CGI continues to evolve, beginners need to have access to user-friendly software that allows them to dive into the world of 3D graphics and animation. In 2023, there are several standout options for CGI software that cater to beginners, providing a stepping stone for learning and creativity. Here, we explore five of the best CGI software choices for beginners:
Blender
Blender has long been a favorite among beginners and professionals alike. This open-source software offers an extensive feature set, making it ideal for 3D modeling, animation, sculpting, and more. What sets Blender apart is its vibrant community and extensive learning resources. You can find countless tutorials, courses, and documentation to help you get started. The user-friendly interface, coupled with its powerful capabilities, ensures that beginners can progress at their own pace and eventually master complex 3D projects.
SketchUp
SketchUp is an intuitive 3D modeling software that shines in architectural and interior design, making it a popular choice for beginners in these fields. Its straightforward tools and interface allow users to create 3D models and visualize spaces quickly. While SketchUp’s primary focus is not on character animation or visual effects, it is an excellent starting point for those interested in architectural modeling, woodworking, or general 3D design. The free version, SketchUp Free, provides essential features for beginners to get started.
Houdini
Houdini, although known for its complexity and extensive capabilities, offers a learning path for beginners through its Houdini Apprentice version. This free software allows users to explore its node-based procedural workflow, a powerful approach for creating complex visual effects. While it may have a steeper learning curve compared to Blender or SketchUp, Houdini is an excellent choice for those who want to dive into the world of visual effects and procedural content creation. Its learning curve may be steep, but the results can be incredibly rewarding.
3DS Max
3DS Max is another software tailored for 3D modeling and animation, suitable for beginners. With an emphasis on ease of use and a vast library of assets, 3DS Max simplifies the process of creating 3D models, scenes, and animations. It is commonly used in game development, architectural visualization, and product design. Autodesk, the company behind 3DS Max, provides extensive documentation and tutorials to help beginners grasp the software’s capabilities.
Maya
Maya, also developed by Autodesk, is a well-regarded 3D animation and modeling software that caters to beginners as well as professionals. It is often favored by those entering the world of character animation, visual effects, and game development. Maya’s user-friendly interface, combined with its comprehensive set of tools for animation, rigging, and rendering, makes it an excellent choice for beginners looking to create 3D characters and animations.
The Future of CGI and 3D Animation


As technology continues to advance, the future of CGI and 3D animation promises to be even more captivating. With each passing year, computing power increases, enabling artists and creators to push the boundaries of realism and creativity. The entertainment industry, including movies, video games, and virtual reality experiences, is set to benefit immensely from these innovations.
One trend that’s gaining momentum is the utilization of real-time rendering, which allows for immediate feedback and adjustments during the creative process. This empowers artists to iterate and refine their work more efficiently, ultimately leading to higher-quality results.
Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning into CGI processes is on the horizon. These technologies can assist in generating complex animations, textures, and even predictive behaviors for characters, streamlining the production process and opening doors to even more imaginative creations.
The convergence of CGI with other technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), offers a new dimension of interactive experiences. These technologies allow users to immerse themselves in digitally generated worlds, blurring the lines between reality and fiction.
Conclusion
CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) and 3D animation have revolutionized the world of visual media and storytelling. They have become integral tools in film, gaming, advertising, architecture, and more industries.
CGI refers to computer-generated visuals, while 3D animation specifically focuses on creating dynamic and lifelike animations in three-dimensional space. They offer many benefits, including realistic and visually appealing graphics, creative freedom, flexibility, cost efficiency, improved workflow and collaboration, and accessibility.
The ability to create highly realistic and immersive visuals and the freedom to explore creative ideas without practical limitations have opened up new possibilities in visual storytelling. CGI and 3D animation provide artists and designers with the tools to bring their imagination to life, creating captivating worlds, characters, and visual effects.
Furthermore, the advantages of these animations extend beyond aesthetics. They offer cost-effective solutions, streamline production workflows, facilitate collaboration, and enable experimentation with different styles and techniques. Their digital nature allows for easy distribution and accessibility across various platforms and devices, reaching a wide audience.
As technology advances, the possibilities for such animations will only expand further, pushing the boundaries of visual creativity and storytelling. Whether it’s a thrilling movie, an immersive video game, or a stunning architectural visualization, they are crucial in captivating and engaging audiences.
CGI and 3D animation have become indispensable tools in the world of visual media, offering endless possibilities for creativity, realism, and immersive storytelling. Their continued development and application in various industries promise a future filled with visually stunning and captivating experiences.


