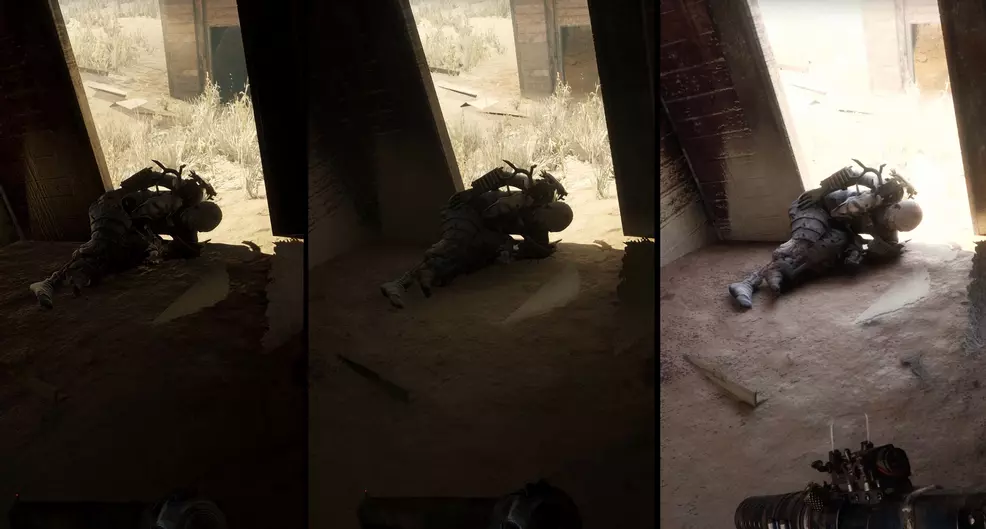
In the realm of animation, the role of lighting is nothing short of transformative. It serves as the painter’s brushstroke on a digital canvas, shaping mood, atmosphere, and narrative. 3D lighting in animation is the art of illuminating three-dimensional virtual environments, bringing life and depth to characters, scenes, and stories. This article delves into the fascinating world of 3D lighting, exploring its definition, various types, fundamental techniques, primary applications in animation, and the indispensable software tools that empower artists to craft captivating visuals. Whether you’re a seasoned animator or an aspiring artist, this guide will shed light on the crucial role that lighting plays in the world of animation.
What is 3D Lighting?
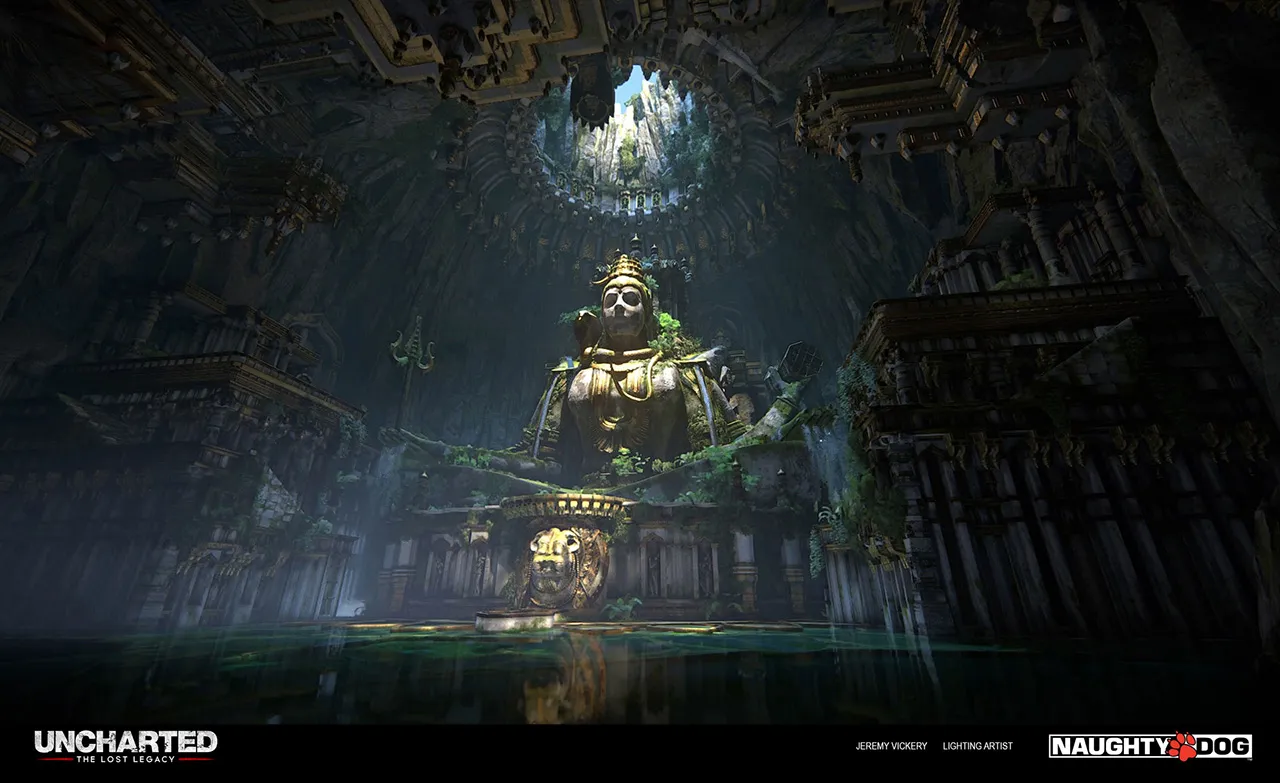


In the realm of 3D animation, lighting is the art of simulating the behavior of light sources within a three-dimensional virtual environment. It plays a pivotal role in creating realistic and visually engaging scenes. 3D lighting involves the placement, intensity, color, and direction of virtual light sources to achieve desired effects. It aims to mimic real-world lighting conditions, considering factors like shadows, reflections, and refractions to bring depth and realism to animated objects and characters. Through the manipulation of light, animators can evoke various moods, emphasize focal points, and guide the viewer’s attention within the animation.
Different Types of 3D Lighting in Animation
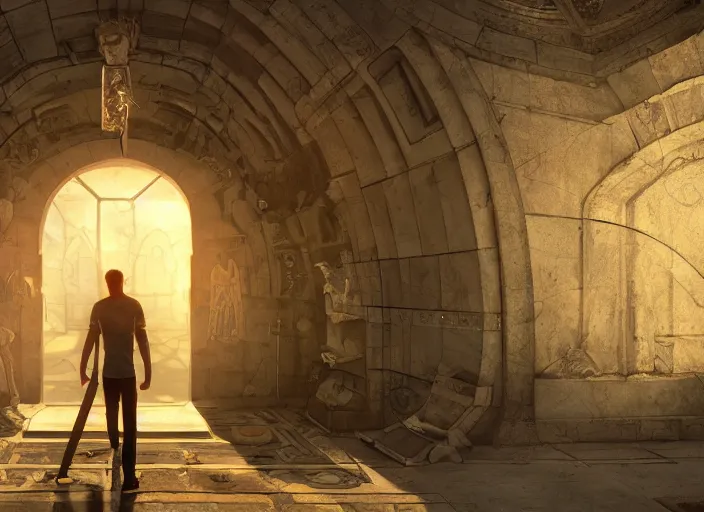


Several types of lighting techniques are employed in 3D animation to achieve specific visual goals:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides overall illumination to a scene, simulating the indirect light that bounces off surfaces. It helps in avoiding overly dark shadows and creating a base level of brightness.
- Directional Lighting: Mimics the effect of sunlight or moonlight, casting parallel rays of light. It is ideal for creating sharp, defined shadows and emphasizing the shape and form of objects.
- Point Lighting: Represents a single light source radiating in all directions, similar to a light bulb or candle. Point lights are useful for creating soft shadows and highlighting specific areas or objects.
- Spot Lighting: Emulates focused beams of light, like that of a flashlight or spotlight. It is employed to draw attention to specific elements within a scene and create dramatic lighting effects.
- Area Lighting: This type of lighting uses an extended source, such as a large rectangular panel. It provides soft, diffused lighting, often used for simulating natural light from windows or creating soft, even illumination.
The Basic Lighting Techniques in a 3D Environment
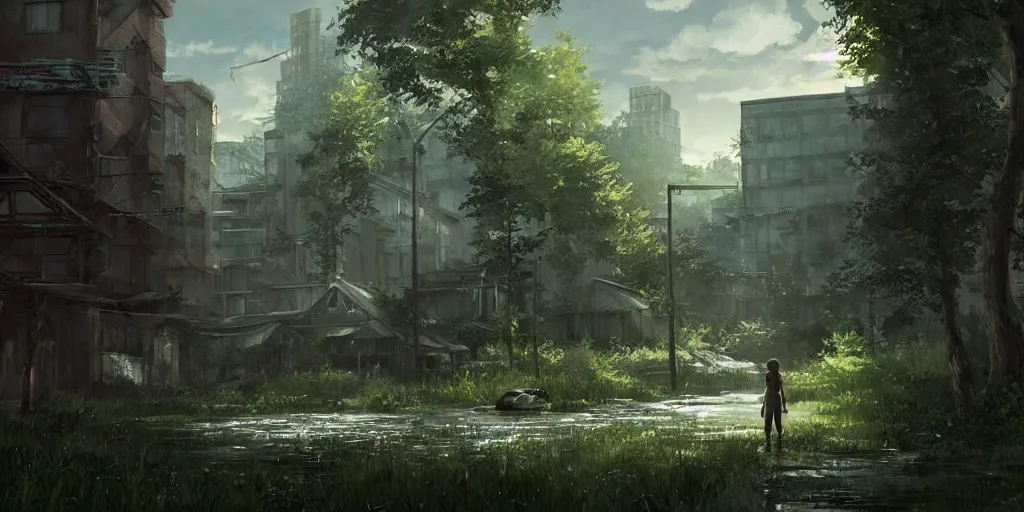


Several fundamental lighting techniques are employed in realistic 3D environment design:
- Key Lighting: This is the primary light source that sets the overall illumination and direction of the scene. It defines the main highlights and shadows on objects and characters.
- Fill Lighting: Fill lights are used to soften shadows created by the key light. They provide secondary illumination and reduce the overall contrast in the scene, enhancing visibility and realism.
- Back Lighting: Backlights are placed behind the subject to create a rim of light around the edges. This separates the subject from the background, adding depth and dimension.
- Rim Lighting: Similar to backlighting, rim lighting specifically highlights the edges of an object or character, accentuating their silhouette and making them stand out from the background.
- Ambient Occlusion: This technique simulates how objects block and occlude light from reaching certain areas. It enhances the perception of depth and realism by adding subtle shading to crevices and corners.
- Global Illumination: Global illumination techniques calculate the indirect lighting in a scene, including light bounces. This adds realism by simulating the way light interacts with surfaces and creates natural-looking soft shadows and color bleeding.
The Main Uses of 3D Lighting in Animation
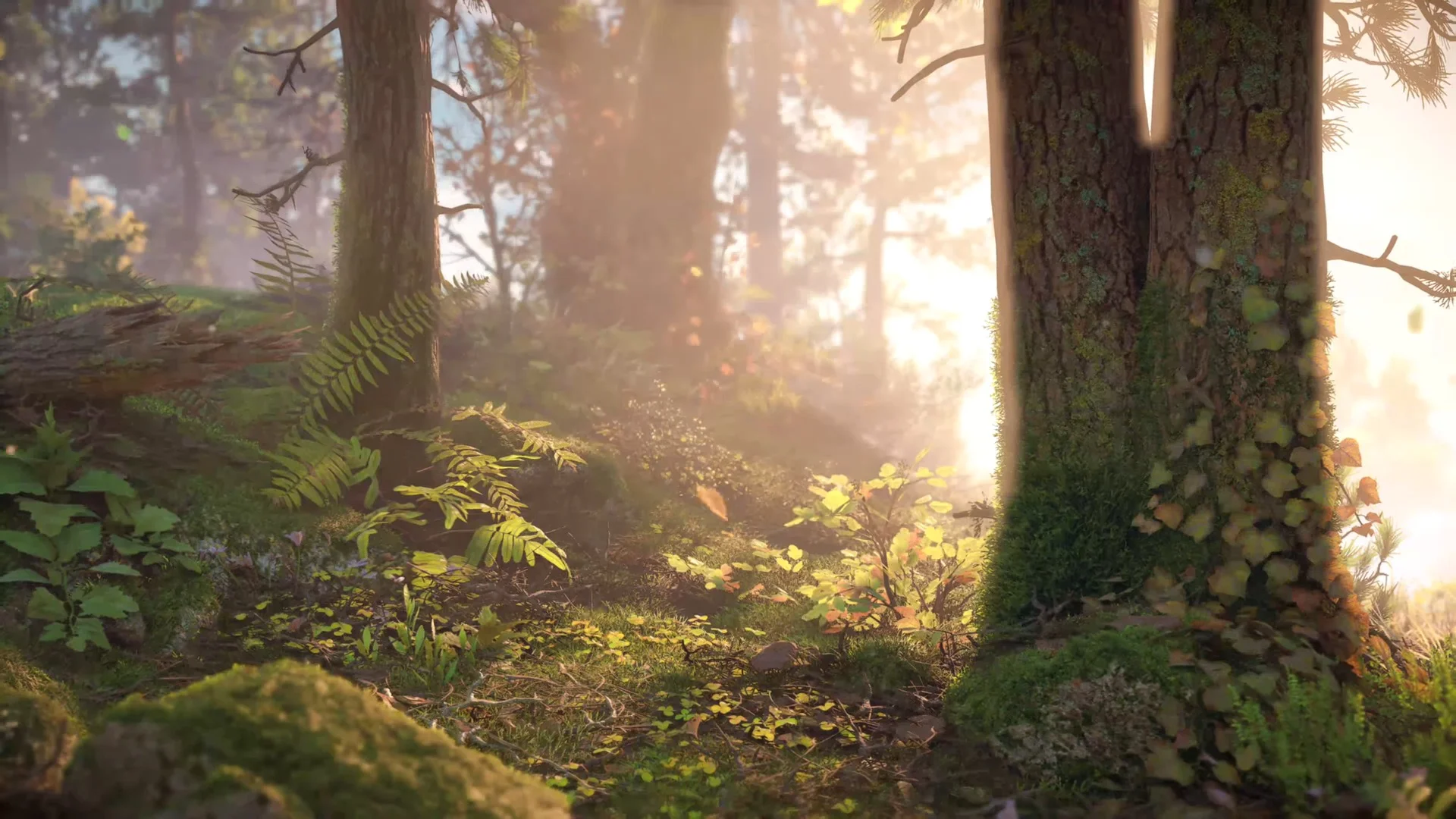


The use of 3D lighting in animation is multifaceted, serving several crucial purposes that enhance storytelling and visual appeal. Here are the main uses of 3D lighting in animation:
Setting Mood and Atmosphere
3D lighting is a potent tool for establishing the mood and atmosphere of a scene. By adjusting the color, intensity, and direction of light, animators can convey emotions and set the tone for a story. For example, warm, soft lighting can evoke feelings of comfort and happiness, while harsh, cool lighting can create tension and suspense.
Defining Shape and Form
Lighting plays a pivotal role in defining the shape and form of 3D objects and characters within a scene. By casting shadows and highlights, it adds depth and dimension, making objects appear more three-dimensional and lifelike. This is crucial for character animation, where lighting accentuates facial expressions and body movements.
Guiding Viewer Focus
Animators use lighting strategically to direct the viewer’s attention to specific elements within a scene. By illuminating important characters or objects and dimming less relevant areas, they guide the viewer’s gaze and emphasize key story elements.
Creating Realism
Realistic lighting is essential for achieving visual authenticity in animation. It mimics the way light behaves in the real world, including the interplay of light and shadow, reflections, and refractions. Realism is particularly important in architectural and product visualization, where accuracy is paramount.
Enhancing Visual Storytelling
3D lighting can convey information and emotions that words and actions alone cannot. It can signify the time of day, weather conditions, or the emotional state of the characters. For example, a stormy, dimly lit scene can symbolize danger or conflict, while a bright, sunlit scene can represent hope and happiness.
Creating Drama and Contrast
Animators use lighting to create dramatic effects and contrast within a scene. Dramatic lighting, such as strong contrasts between light and shadow, can add intensity and suspense to pivotal moments in a narrative.
Highlighting Texture and Detail
Lighting is instrumental in showcasing the textures and intricate details of objects and characters. It accentuates surface imperfections, materials, and textures, making the 3D models appear more tactile and convincing.
Simulating Special Effects
3D lighting is often used to simulate special effects like fire, explosions, and magical spells. By manipulating lighting effects, animators can achieve visually striking and immersive sequences.
Creating Cinematic Visuals
Lighting in animation is akin to cinematography in live-action filmmaking. It enables animators to compose visually stunning shots, frame scenes artistically, and craft cinematic storytelling experiences.
3D lighting Software Programs Used in the Animation

In the world of animation, various software programs are instrumental in achieving impressive 3D lighting in animation and creating visually captivating scenes. Here are some prominent 3D lighting software programs widely used in the animation industry:
- Autodesk Maya: Maya is a comprehensive 3D animation and modeling software that offers a rich set of lighting and rendering tools. It is a favorite among animators for its versatility and integration with other Autodesk products.
- Pixar RenderMan: RenderMan, developed by Pixar, is a powerful rendering software used in conjunction with various 3D animation programs. It’s known for its ability to produce photorealistic lighting and shading effects and has been utilized in numerous blockbuster films.
- Chaos Group V-Ray: V-Ray is a popular rendering engine known for its advanced lighting and rendering capabilities. It seamlessly integrates with Autodesk Maya and other 3D software, offering photorealistic rendering solutions.
- SideFX Houdini: Houdini is renowned for its procedural approach to 3D animation and visual effects. It boasts a robust lighting and rendering toolset, making it a top choice for artists looking to create complex, dynamic lighting setups.
- Maxon Cinema 4D: Cinema 4D is a versatile 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software. It offers a user-friendly interface and robust lighting tools suitable for motion graphics and visual effects.
- Blender: Blender is a powerful open-source 3D software that includes a comprehensive lighting and rendering system. Artists and hobbyists favor it for its flexibility and active community support.
- Luxion KeyShot: KeyShot is a real-time 3D rendering and animation software that excels in product visualization and industrial design. It provides a user-friendly interface and a wide range of lighting options.
- Redshift: Redshift is a GPU-accelerated rendering engine known for its speed and efficiency. It’s often used with software like Autodesk Maya and Cinema 4D, delivering high-quality lighting and rendering results.
- Foundry Katana: Katana is a lighting and rendering software designed for complex lighting workflows in visual effects and animation studios. It streamlines the lighting and look development processes.
- Arnold: Arnold is a rendering engine developed by Autodesk, known for its ability to produce realistic lighting and shading effects. It’s integrated with software like Maya and Houdini.
- Octane Render: Octane Render is a GPU-based rendering engine popular for its speed and quality. It offers advanced lighting and rendering solutions, making it a favorite among artists and studios.
- Adobe After Effects: While primarily recognized for compositing and motion graphics, After Effects includes robust lighting and shading effects that are useful for enhancing animations and creating atmospheric visuals.
Conclusion
In the vast and ever-evolving realm of animation, 3D lighting in animation stands as both a science and an art form. It’s the invisible hand that breathes life into pixels, turning digital landscapes into immersive, believable worlds. From defining the mood and atmosphere to guiding the viewer’s gaze, the uses of 3D lighting in animation are as diverse as the stories it helps tell.
Whether it’s the soft, warm glow of a cherished memory or the stark, dramatic contrast of a thrilling action sequence, 3D lighting is the magician’s wand that transforms mere polygons into emotional experiences. As the animation industry continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible, the importance of 3D lighting in captivating audiences and conveying narratives remains an enduring truth in this mesmerizing craft.


