In the world of game development, 3D art styles have become an essential part of creating immersive and engaging experiences for players. With advancements in technology, the possibilities for creating stunning 3D visuals have expanded greatly, giving game developers a vast range of options to choose from. In this article Polydin game art studio, we will explore the top 5 3D art styles used in game development today, along with an overview of the software and technologies used to create them.
What is 3D Art?
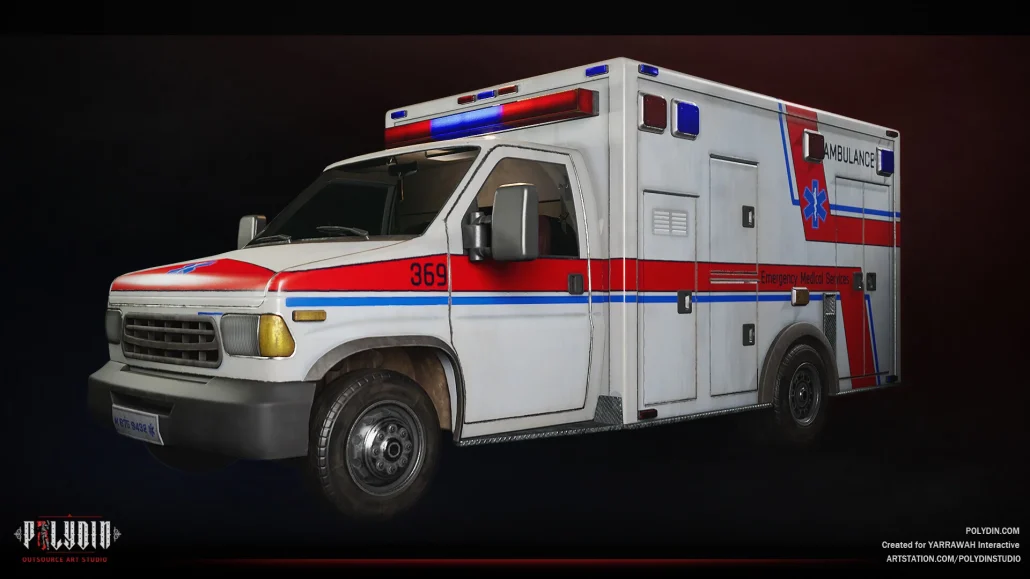

3D art production is a form of computer graphics that uses three-dimensional representations of objects and environments to create digital art. Unlike traditional 2D art, which is created on a flat canvas, 3D art allows artists to create objects and characters that have depth and can be viewed from multiple angles. This makes 3D art particularly useful for video games, movies, and other forms of digital media that require immersive and interactive environments.
To create 3D art, artists use specialized software that allows them to manipulate digital models of objects and characters in three dimensions. They can create textures, add lighting and special effects, and even program the models to move and interact with their environment. The result is a dynamic and engaging form of digital art that has become increasingly popular in recent years.
Top 3d Game Art Styles
In the dynamic world of 3D gaming, art styles play a pivotal role in shaping the visual identity and immersive experience of a game. From lifelike realism to whimsical fantasy realms, the choice of art style can evoke a wide range of emotions and set the tone for the entire gaming experience. Let’s delve into some of the top 3D art styles that have captivated players and developers alike.
Realism
Realism in 3D game art aims to replicate the natural world with astonishing accuracy, creating environments and characters that closely resemble their real-life counterparts. Realistic art styles prioritize attention to detail, texture fidelity, and lighting effects to create immersive and believable game worlds. From intricately modeled landscapes to meticulously crafted character animations, realism transports players into virtual realms that blur the line between fantasy and reality.
Low Poly
Low poly art styles embrace simplicity and abstraction, using geometric shapes and minimalist textures to create visually striking environments and characters. Characterized by angular forms and bold colors, low poly art styles offer a stylized interpretation of reality that emphasizes creativity and expression over strict adherence to realism. Despite their minimalistic appearance, low poly games can evoke a sense of nostalgia and charm, harkening back to the early days of 3D gaming while showcasing the timeless appeal of stylized aesthetics.
Fantasy Realism
Fantasy realism blends elements of the fantastical with the grounded aesthetics of realism, creating worlds that are both familiar and fantastical. In fantasy realism art styles, artists draw inspiration from real-world environments and architecture while infusing them with magical elements, mythical creatures, and otherworldly landscapes. By seamlessly integrating elements of fantasy into realistic settings, fantasy realism art styles offer a captivating blend of imagination and immersion that transports players to enchanting realms filled with wonder and adventure.
Anime
Anime art styles draw inspiration from Japanese animation and manga, featuring exaggerated proportions, vibrant colors, and expressive character designs. In 3D gaming, anime art styles capture the distinctive aesthetic of anime while leveraging the depth and immersion afforded by three-dimensional environments. From whimsical fantasy worlds to futuristic sci-fi settings, anime art styles bring to life captivating narratives and dynamic characters that resonate with fans of anime and gaming alike.
Top 5 3D Art Styles in Game Development
When it comes to creating 3D games, there are a variety of art styles that game developers can choose from. Each style can impact the game’s overall look and feel, making it an important decision in the development process. We’ll be taking a look at the top 5 3D art styles in game development, including their unique characteristics, popular games that use them, and what makes them stand out.
Cartoon
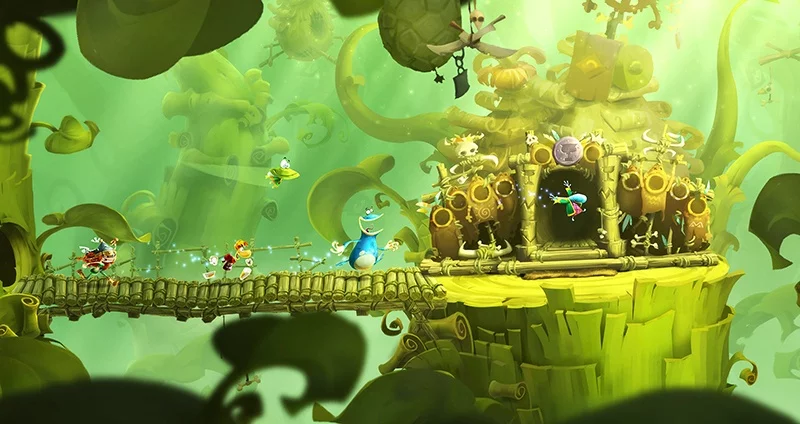

Cartoon-style 3D art, also known as toon shading, is one of the popular 3D art styles that imitates the look and feel of traditional 2D animation. The style is characterized by its simplified forms, bold outlines, and bright colors, often used to create a fun and whimsical atmosphere. One of the main benefits of using cartoon-style 3D art is that it can help to create a more accessible and approachable game for players of all ages.
Cartoon-style 3D art is commonly used in a wide range of game genres, including platformers, action games, and even first-person shooters. Games like Fortnite and Overwatch are notable examples of the style’s popularity in the industry. The style is also often used in educational and edutainment games, as it can help to make complex concepts more digestible and engaging for players. Additionally, cartoon-style 3D art can be used to create marketing materials, such as trailers and promotional images, to help promote a game’s launch.
Realism
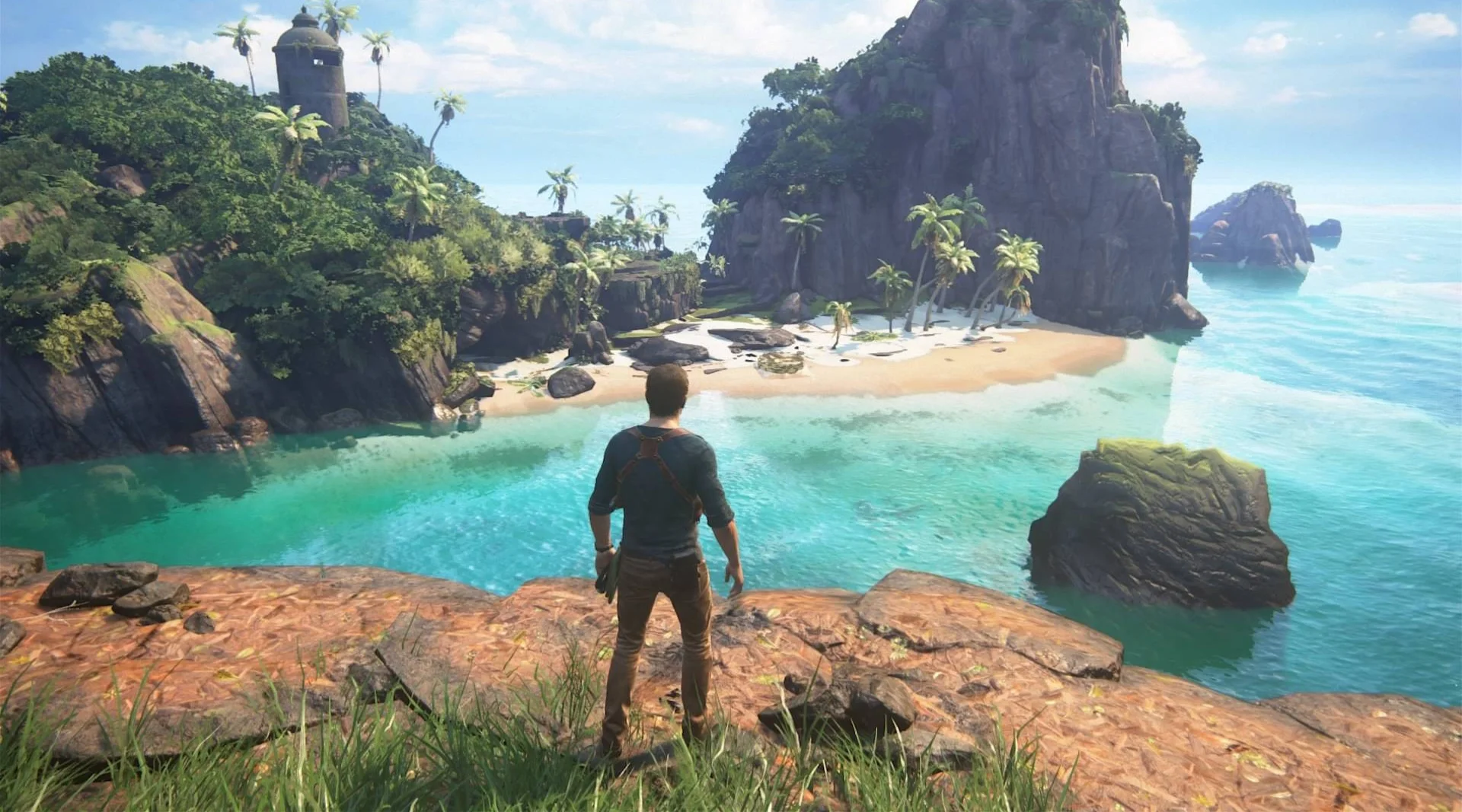

Realism is a 3D art style that aims to replicate real-life environments, objects, and characters with high accuracy. This art style is often used in games that strive to provide a more immersive experience, such as simulation games or first-person shooters. Realism can involve detailed textures, intricate lighting, and advanced physics to make the game world feel more lifelike.
Realism is not only limited to creating realistic environments and characters but it is also used for recreating historical sites and events, such as museums or educational software. Medical software and training programs also use realism in 3D art to simulate procedures and surgeries. The automotive and aerospace industries use realism in 3D art to create visualizations of their products, allowing them to test the design, make improvements, and visualize the final product. 3D artists use realism in film and television to create special effects, such as explosions or realistic monsters.
Fantasy Realism

Fantasy realism is a 3D art style that combines elements of realism with fantastical or magical elements to create a believable yet imaginary world. It is often used in games that take place in fictional worlds or alternate realities. This style aims to create an immersive experience for the player by bringing them into a recognizable and otherworldly world.
Fantasy realism is commonly used in role-playing games (RPGs) and massively multiplayer online games (MMOs). Examples of such games include The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim and Age of Conan. This art style is also often used in the creation of character designs, environments, and objects in games. The goal of fantasy realism is to create a world that feels familiar yet still allows for the suspension of disbelief required in a fantasy setting.
Low Poly/Cell Shading
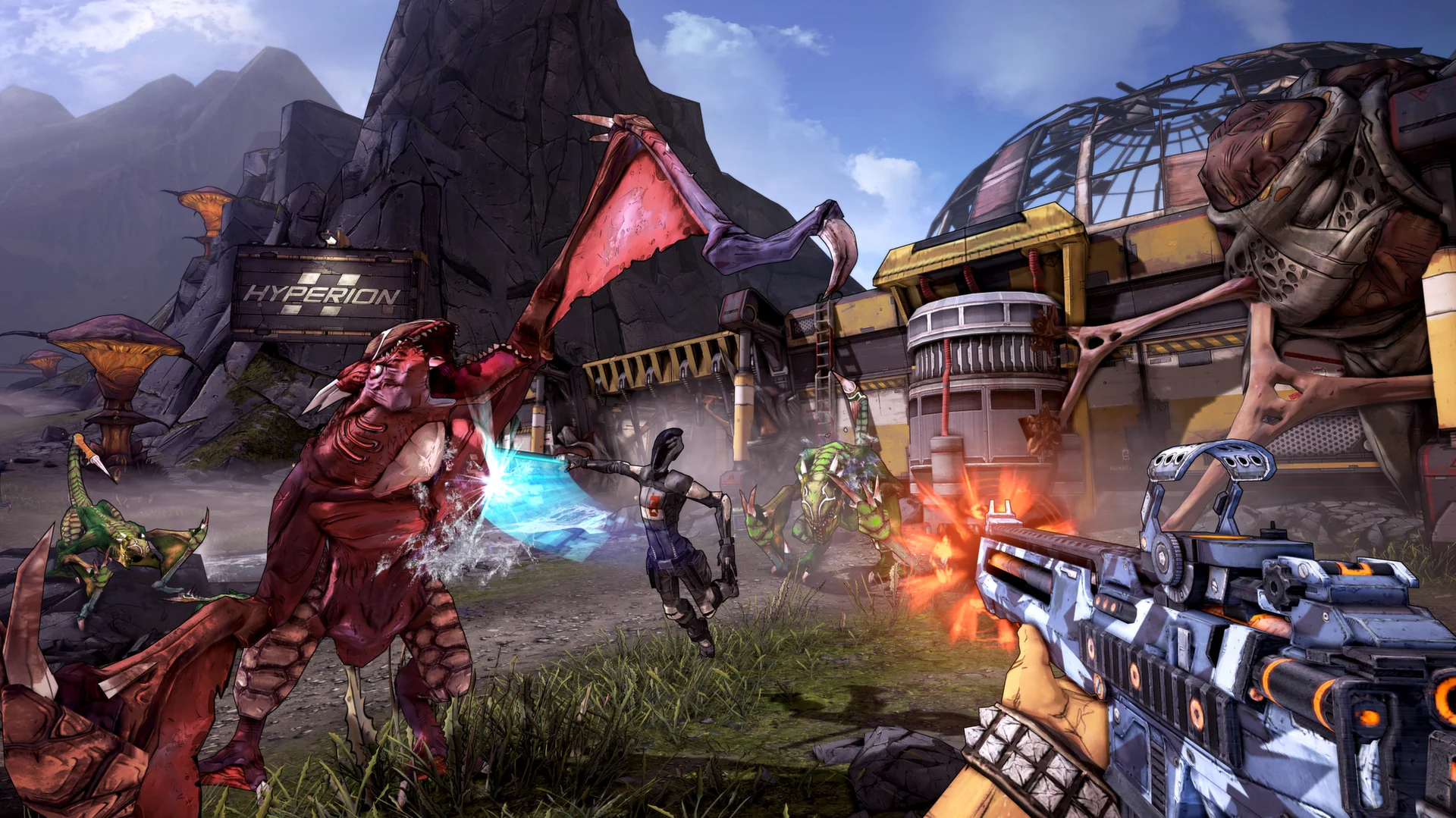

Low Poly/Cell Shading is a 3D art style that is popular for its simplistic, angular, and polygonal shapes. It is often used in games that are designed to look playful, retro, or cartoonish, but it can also be used to create stunningly beautiful and immersive environments. One of the most popular application areas for this style is adventure games, platformers, and puzzle games, as it can give these types of games a unique and stylized look that sets them apart from more realistic games.
Another popular application area for Low Poly/Cell Shading is in simulation games, such as farming, city-building, and management games, as it can make these games more approachable and visually appealing. The style is also used in some first-person shooter games, especially those with a futuristic or sci-fi theme, to give the game world a distinct, stylized look. Overall, Low Poly/Cell Shading is a versatile and popular 3D art style used in various game genres and applications.
Hand-Painted
Hand-Painted is a 3D art style that mimics traditional painting techniques. This style is often used in games to create a unique, stylized look with a high level of detail. Unlike other 3D art styles, hand-painted textures are created by an artist using a stylus and tablet rather than generated by a computer program.
Hand-Painted is a popular choice for games with a fantasy or cartoonish look. It allows for high creativity and flexibility, as artists can use a wide range of brush strokes and color palettes to achieve the desired effect. This style is often seen in RPGs, platformers, and adventure games, where the focus is on exploration and storytelling rather than realistic graphics. Games like “World of Warcraft” and “Hollow Knight” are excellent examples of Hand-Painted 3D art styles, and their success proves how this style can enhance the overall gaming experience.
Stylized
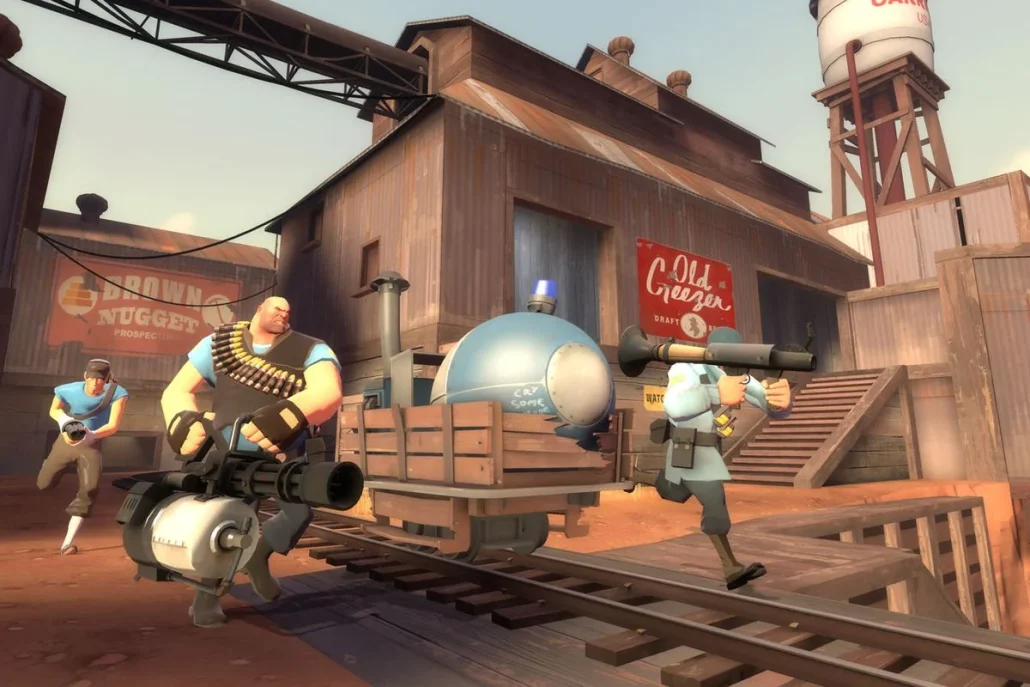

Stylized 3D art is a popular art style that emphasizes exaggerated or simplified shapes, bright colors, and non-realistic textures. This art style can be seen in various games, from indie titles to large-scale AAA games. Stylized art is often used in games where realism is not the primary goal, and the game world has a unique or fantastical feel to it.
One of the main advantages of using a stylized art style is that it can be used to create a distinctive and memorable game world. This art style is often used in fantasy or sci-fi games, where a unique and imaginative world needs to be created. Stylized art can also be used to create games with a more light-hearted or humorous tone, as it can help to create a sense of fun and playfulness. Some popular examples of games that use stylized art include Fortnite, Team Fortress 2, and The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild.
What is stylized art in games?
Stylized art in games refers to a deliberate artistic approach that emphasizes exaggerated, abstract, or non-realistic visuals, often departing from strict realism. Stylized art focuses on conveying mood, emotion, and aesthetic appeal through bold colors, simplified shapes, exaggerated proportions, and imaginative designs. This artistic style allows developers to create visually striking and memorable game worlds that evoke a sense of fantasy, whimsy, or surrealism, while still conveying the intended gameplay experience and narrative themes.
Most Common 2D Game Art Styles
1. Flat
Flat art emphasizes simplicity with clean lines, minimal shading, and bold, uniform colors. It creates a sleek, modern aesthetic that is easy to read visually, making it an ideal choice for casual and mobile games. Titles like Monument Valley showcase this style, blending elegance with functional design to enhance gameplay.
2. Vector
Vector art uses scalable, sharp shapes and vibrant colors to produce crisp visuals that remain clear across all resolutions. This style is often used in mobile games like Angry Birds and web-based titles, thanks to its versatility and lightweight nature. The use of bright, eye-catching designs keeps players engaged while maintaining a polished look.
3. Geometric Art
Geometric art relies on abstract shapes and patterns to craft unique visual identities. This minimalist style often features triangles, circles, and other basic forms to build environments and characters. Games like Thomas Was Alone use geometric art to convey a distinct aesthetic while focusing on storytelling and gameplay mechanics.
4. Pixel
Pixel art is a nostalgic style that harkens back to the early days of gaming. It uses small, square pixels to create detailed sprites and environments. Games like Celeste and Stardew Valley showcase the charm of pixel art, blending retro visuals with modern gameplay innovations. This style often evokes a sense of nostalgia while offering flexibility for indie developers.
5. Cartoon
Cartoon art exaggerates proportions, expressions, and movements to create a playful and approachable style. This art style is common in family-friendly games like Cuphead and Castle Crashers, combining humor and whimsy with vivid, hand-drawn aesthetics. The expressive nature of cartoon art makes it ideal for storytelling and engaging a broad audience.
6. Cel Shading
Cel shading gives a hand-drawn, comic-book appearance by using bold outlines and flat shading. Games like The Legend of Zelda: The Wind Waker and Borderlands use cel shading to create striking, memorable visuals that stand out. This style offers a unique blend of realism and stylization, making it a favorite for games with a strong narrative focus.
7. Monochromatic
Monochromatic art focuses on a single color or limited tones to create dramatic and atmospheric visuals. Games like Limbo use this style to convey mood and emotion, often enhancing darker or more experimental narratives. By stripping away color complexity, monochromatic art emphasizes form, light, and shadow, creating striking contrasts that resonate with players.
These 2D art styles showcase the wide range of creative possibilities available to developers, offering unique ways to capture players’ attention, evoke emotion, and enhance gameplay. Whether minimalistic, vibrant, or nostalgic, each style brings its own character to the gaming experience.
Realistic vs. Stylized Art Style in Game
- Realistic Art Style:
- Realistic art aims to depict game worlds, characters, and environments in a manner that closely resembles reality. This approach prioritizes detailed textures, accurate lighting, and lifelike proportions to create immersive and believable visuals.
- Realistic art styles are often used in games that aim for authenticity, immersion, and simulation, such as military shooters, sports simulations, and historical reenactments.
- Advantages of realistic art include its ability to create a sense of immersion and authenticity, as well as its potential for showcasing technical prowess and graphical fidelity.
- Challenges of realistic art include the high level of detail required, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive to produce, as well as the risk of uncanny valley effects when striving for hyper-realism.
- Stylized Art Style:
- Stylized art takes a more interpretive and expressive approach to visual design, often exaggerating or simplifying elements to convey a distinct aesthetic or mood. This approach allows for greater creativity, imagination, and artistic freedom.
- Stylized art styles can vary widely in their execution, ranging from cartoonish and whimsical to minimalist and abstract. They may draw inspiration from various art movements, cultures, and design philosophies.
- Stylized art is commonly used in games with fantastical, surreal, or imaginative themes, such as fantasy adventures, platformers, and indie titles.
- Advantages of stylized art include its flexibility, versatility, and ability to evoke emotions and convey narrative themes through visual symbolism and metaphor.
- Challenges of stylized art include the need for strong artistic direction and consistency to maintain coherence within the game world, as well as the potential for subjective interpretation and stylistic preferences among players.
In summary, while both realistic and stylized art styles have their own unique strengths and challenges, the choice between them ultimately depends on the creative vision, thematic goals, and technical considerations of the game project. Developers may opt for realism to achieve authenticity and immersion, or they may embrace stylization to unleash their creativity and create visually distinct and memorable game experiences.
3D Art Forms Software and Technologies

In order to create 3D art styles, a variety of software and technologies are used. Some of the most popular ones include:
- Autodesk Maya: This is a 3D computer graphics software used for creating animated films, TV shows, video games, and more. It is commonly used in the film and TV industry, as well as in game development.
- Blender: This is a free and open-source 3D creation software. It is used for creating 3D models, animations, and even video games. It is a popular choice for indie game developers due to its accessibility and powerful features.
- ZBrush: This is a digital sculpting tool that is used for creating high-resolution models. It is commonly used in the film and game industry for creating characters, creatures, and other detailed assets.
- Substance Painter: This is a texture painting software that allows artists to create high-quality textures for 3D models. It is often used in game development to create realistic and detailed textures for characters and environments.
- Unity: This is a game engine that is commonly used for creating 3D games. It allows developers to create and edit 3D models, import assets, and program gameplay mechanics all within one software.
- Unreal Engine: This is another popular game engine that is used for creating 3D games. It features powerful tools for creating and editing 3D models and advanced lighting and physics systems.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality: With the rise of VR and AR, new software and technologies are being developed to create immersive 3D experiences. Tools such as Unity and Unreal Engine can be used to create VR and AR experiences, while software like Tilt Brush and Gravity Sketch allows artists to create 3D models in a virtual environment.
As technology advances, new software and technologies will continue to emerge, providing even more possibilities for creating 3D art styles.
How do I Find my 3D Art Style?

Discovering your unique 3D art style involves a blend of exploration, practice, and self-awareness. Start by immersing yourself in various art forms, not just limited to games. Study different artistic movements, from traditional to contemporary, and observe how artists utilize shapes, colors, and forms. Experiment with different techniques, tools, and software to understand what resonates with you. Through this exploration, you can begin to identify elements that capture your interest.
Practice is essential. Consistently create 3D models in different styles to understand your strengths and preferences. Embrace iterations and don’t be afraid to deviate from your comfort zone. As you practice, you might notice patterns emerging in your work – certain shapes, textures, or color palettes that recur. These patterns are the building blocks of your unique style.
Self-awareness is key. Reflect on your own personality, experiences, and emotions. These aspects can influence the tone and mood of your art style. Additionally, solicit feedback from peers and mentors. Constructive criticism can help you refine your style and identify areas for growth.
Different Approaches to 3D Game Art

In the realm of 3D game art, several distinct approaches and disciplines come into play, each contributing to the overall visual and interactive experience of a game.
Modeling
Modeling is the foundation of 3D game art. It involves creating three-dimensional objects or characters using specialized software. Modelers sculpt the shape, structure, and geometry of in-game elements, defining their appearance and interactions within the virtual world.
Animation
breathes life into 3D game characters and objects. Animators manipulate these models to produce lifelike movements, actions, and behaviors. Whether it’s the graceful flight of a dragon, the fluid combat of a hero, or the subtle expressions of an NPC, animation is crucial for conveying realism and immersion.
Texturing
is all about giving surfaces and materials their visual identity. Texture artists apply images, patterns, and details to 3D models, enhancing their realism and aesthetics. Textures define everything from the roughness of a rock to the shimmering scales of a dragon.
Rendering
Rendering is the process of creating the final 2D images or frames from 3D scenes. It involves lighting, shading, and camera settings to produce visually appealing and technically efficient graphics. The rendering stage is where the artistry and technical expertise of the game artist converge to create stunning visuals.
These disciplines work in harmony to craft the captivating worlds and characters players encounter in 3D games. Whether it’s the meticulous modeling of intricate environments, the fluidity of character animations, the attention to detail in textures, or the final rendering that brings it all to life, each aspect contributes to the immersive experience that defines modern 3D gaming.
Art Style in Different Game Genres
The art style of a video game is a crucial element that shapes the player’s experience and engagement. Each game genre leverages distinct artistic approaches to enhance gameplay, evoke emotions, and immerse players in unique worlds. Whether it’s the intricate details of an RPG or the vibrant simplicity of a Match-3 game, the visual aesthetics are tailored to complement and elevate the core mechanics of the genre.
RPG
The art style in RPGs is often immersive and detailed, designed to draw players into expansive, richly crafted worlds. These games typically feature highly detailed character designs, intricate environments, and a mix of fantastical and realistic elements. Games like “The Witcher” and “Final Fantasy” showcase elaborate costumes, diverse landscapes, and a blend of mythical and real-world influences. The goal is to create a visual narrative that supports the deep, story-driven gameplay, allowing players to fully inhabit their characters and the game world.
Tower Defense
Tower defense games prioritize clarity and functionality in their art styles. The visuals are often clean and straightforward to ensure that players can easily discern different units, enemies, and defensive structures. Aesthetics can range from cartoonish and whimsical, as seen in “Plants vs. Zombies,” to more realistic or futuristic, like “Defense Grid.” The key is to balance engaging, appealing visuals with clarity, ensuring that the player can strategize effectively without being overwhelmed by visual noise.
Platformer
Platformer games usually feature bright, colorful, and often stylized art to create visually appealing and memorable worlds. The art style is typically more playful and exaggerated, with a focus on smooth, fluid animation to support the fast-paced, jumping mechanics central to the genre. Classic examples like “Super Mario” and “Sonic the Hedgehog” utilize vibrant color palettes and distinct character designs that are instantly recognizable and contribute to the game’s charm and appeal.
Survival
Survival games often employ a gritty, realistic art style to enhance the tension and immersion of the gameplay. The environments are usually detailed and atmospheric, aiming to convey a sense of danger and unpredictability. Games like “The Forest” and “Rust” use muted color schemes and realistic textures to create a sense of realism and urgency, making the player feel truly vulnerable and invested in their struggle for survival.
Real-Time Strategy
RTS games often utilize a top-down or isometric perspective, with art styles that prioritize readability and strategic clarity. The visuals need to distinguish between different unit types, buildings, and resources at a glance. Games like “StarCraft” and “Age of Empires” balance detailed, thematic art with functional design, ensuring that players can quickly and accurately interpret the battlefield while also enjoying the visual representation of their strategies.
City-Building
City-building games often feature detailed, realistic art styles that allow players to see their cities grow and evolve over time. These games, like “SimCity” and “Cities: Skylines,” focus on creating visually appealing urban landscapes with a high level of detail and realism. The art style supports the game’s emphasis on planning and development, providing a satisfying visual feedback loop as players see their cities flourish.
Match-3
Match-3 games typically employ bright, colorful, and highly stylized art to create a visually stimulating and engaging experience. The designs are often simple but attractive, with an emphasis on clear, distinct shapes and colors to facilitate quick recognition and matching. Games like “Candy Crush” and “Bejeweled” use vibrant, playful visuals to keep players engaged and entertained, making the gameplay both addictive and visually pleasing.
The Art of Storytelling Through 3D Art
3D art doesn’t just depict a game’s world—it communicates its story, atmosphere, and emotional tone. Every element of a 3D game can contribute to storytelling, whether through environmental details, character design, or visual composition.
- Environmental Storytelling
World design is a powerful narrative tool. Environments can convey history, culture, and mood without a single line of dialogue.
- Examples:
- In The Last of Us, abandoned buildings, overgrown vegetation, and personal belongings scattered in homes tell the story of a world ravaged by disaster.
- In Hollow Knight, the crumbling ruins and desolate halls of Hallownest hint at the kingdom’s tragic downfall.
- Props and Details
Small, seemingly inconsequential objects can reveal backstory and character motivations.
- Examples:
- A child’s drawing pinned to a wall in Bioshock suggests the presence of families in Rapture before its collapse.
- A bloodstained sword in Elden Ring might imply a battle’s outcome, adding layers to the environment’s lore.
- Emotional Engagement
Through carefully crafted 3D art, developers evoke emotions that enhance the narrative.
- Lighting and Shadows: Dark, shadowy corners create suspense in horror games like Resident Evil, while warm sunlight streaming through windows provides hope in games like Firewatch.
- Color Palettes: Muted colors in Death Stranding emphasize loneliness, while vibrant hues in Journey symbolize discovery and renewal.
How do I Choose an Art Style for a Video Game?

Selecting an art style for a video game is a pivotal decision that impacts the overall player experience. The choice should align with the game’s narrative, mechanics, and target audience. Begin by understanding the game’s genre and theme. Is it an action-packed adventure or a serene puzzle game? The art style should complement the intended emotional impact.
Consider the capabilities of your development team and the technology you’re using. A complex, realistic art style might not be feasible if you have limited resources. On the other hand, a stylized or minimalist approach can make a game visually striking even with limited technical prowess.
Know your target audience. A cartoonish, vibrant style might appeal to younger players, while a darker, more realistic style could resonate with mature audiences. Research similar games and examine the art styles that have been successful in those contexts. However, don’t be afraid to inject your unique vision into the chosen style.
Ultimately, the art style should enhance the gameplay experience, immersing players in the game world. A well-chosen art style can become an integral part of the game’s identity, leaving a lasting impression on players long after they’ve put down the controller.
The Impact of Art Direction on 3D Game Design
Art direction shapes every aspect of a 3D game’s visuals, acting as a guiding force for aesthetic decisions and ensuring that all elements work together cohesively. Its influence extends beyond visuals into gameplay, world-building, and player experience.
- Establishing a Visual Style
Art direction determines the overall tone and style of a game. It defines whether a game leans toward hyper-realism, stylization, or experimental visuals.
- Realistic Art Direction: Games like Cyberpunk 2077 and Red Dead Redemption 2 rely on hyper-realistic art to immerse players in believable worlds. Every detail, from textures to lighting, aims to replicate real-life visuals and create a grounded experience.
- Stylized Art Direction: In games like Overwatch or Sea of Thieves, exaggerated proportions, vibrant colors, and bold shapes create a distinctive, memorable aesthetic. This approach often appeals to broader audiences and allows for more creative freedom.
- Enhancing Player Immersion
A consistent and thoughtful art direction ensures that every asset, from characters to environments, fits within the game world. This consistency creates a seamless experience, helping players feel like they’re part of the story.
- Immersive Lighting and Atmosphere: Lighting plays a crucial role in setting the mood. In Control, the eerie red hues of the Hiss-infected areas signal danger, while soft lighting in safe zones provides a sense of relief.
- Texture and Detail: Small, detailed elements like weathered walls or scuffed armor give environments and characters a lived-in feel, reinforcing the believability of the game world.
- Guiding Player Focus
Art direction uses visual elements like contrast, color, and composition to guide players without explicit instructions.
- Bright colors or high contrast often highlight key paths or interactable objects, as seen in Uncharted.
- Subtle details, like the placement of light sources or leading lines in architecture, can naturally direct players toward objectives without breaking immersion.
Emerging Trends in 3D Art Styles
As 3D game development continues to evolve, new technologies and creative approaches are transforming the way art is crafted and presented in video games. These advancements not only enhance the visual appeal of games but also open up new possibilities for immersive experiences. Here are some of the most notable emerging trends in 3D art styles shaping the future of gaming:
High-Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI)
HDRI is a technique that enhances the contrast and brightness range in 3D environments, creating more lifelike and visually stunning graphics. By capturing a greater range of light intensities, HDRI allows for realistic lighting and shading, which adds depth and dimension to 3D models and scenes. This trend is becoming increasingly popular in game design, as it delivers richer visual experiences, especially in high-fidelity games.
Immersive 3D Art in VR and AR
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are pushing 3D art into new realms of interactivity. Artists must now consider how objects and environments behave in a fully immersive space where players can interact with every angle and element. The rise of VR/AR games has led to innovative 3D modeling techniques that prioritize high immersion, such as real-time environment changes, physics-based interactions, and highly detailed character models that can be viewed up close.
Real-Time Ray Tracing
Real-time ray tracing has revolutionized the realism of 3D games by simulating how light interacts with objects in real-time. Reflections, shadows, and global illumination now respond dynamically to changes in the environment, creating highly realistic visuals. This trend is increasingly adopted in AAA games, where realistic lighting effects are essential for creating immersive worlds. As hardware technology advances, more studios are integrating ray tracing to enhance their game’s visual fidelity.
Dynamic Environments and Weather Systems
Creating responsive and evolving 3D environments is a growing trend, particularly in open-world games. Dynamic weather systems, shifting day-night cycles, and terrain deformation are becoming more common, adding realism and variety to 3D game worlds. These systems create a living, breathing environment where changes affect gameplay, such as altering visibility during storms or affecting a player’s traversal during different times of the day.
Comparative Analysis of 2D vs. 3D Art Styles
The choice between 2D and 3D art styles can significantly impact the gameplay experience, visual aesthetics, and overall design of a game. While both styles have their strengths, understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right approach for your game project. Below is a comparative analysis of key aspects between 2D and 3D art styles:
- Visual Depth: 2D art, while visually appealing, typically presents a flatter image, which can work well for games with simpler aesthetics or a stylized look. In contrast, 3D art offers depth and realism, making it suitable for games where immersion in a rich, lifelike world is key. 3D art allows for more dynamic camera movements and angles, creating a more interactive experience, especially in first-person and third-person games.
- Animation Complexity: 2D games often rely on frame-by-frame animation, which can be more labor-intensive, whereas 3D models allow for rigging and skeletal animation systems. In 3D games, character movements and interactions are more fluid and adaptable, making them ideal for games with complex animations like combat systems or physics-based mechanics.
- Resource Requirements: 3D game development generally demands more processing power and technical expertise due to the need for detailed models, textures, and lighting. Meanwhile, 2D games, though often less resource-intensive, can offer unique styles and a retro aesthetic, appealing to indie developers or genres like platformers and strategy games.
- Artistic Flexibility: While 2D art can create vibrant, stylized worlds that are visually distinctive, 3D art allows for more versatility in genres like action, adventure, and simulation. 3D games can balance between realism and stylization, depending on the artistic direction, whereas 2D games tend to be more constrained by the chosen style (e.g., pixel art, vector graphics).
Read Also: Game Art Outsourcing
Comparing Western vs. Eastern 3D Animation Art Styles
The world of 3D animation is as diverse as the cultures that inspire it. Western and Eastern studios have long developed distinct visual identities in animation and game art. Now, with AI tools becoming part of the creative pipeline, these differences are evolving in new and unexpected ways.
Western 3D animation often emphasizes realism, weight, and texture. Studios like Pixar and DreamWorks build worlds filled with detailed environments, complex lighting systems, and physically accurate character motion. Proportions tend to be more grounded, even in stylized works, and characters often follow anatomical logic that supports fluid, believable movement.
Eastern 3D animation, especially from Japan and South Korea, leans heavily into stylization. Influenced by anime aesthetics, characters may have exaggerated features, simplified textures, and minimal shading to preserve a 2D look in 3D space. Color palettes are usually bolder, and motion is often more symbolic than realistic. The focus is on visual clarity, dramatic silhouettes, and emotional resonance, rather than physical realism.
In game development, these differences are just as visible. A Western RPG like The Witcher may aim for gritty detail and lifelike terrain, while a title like Genshin Impact opts for cel-shaded models, expressive eyes, and smooth, stylized effects.
Using AI in 3D Game Art Creation
Artificial intelligence is transforming the way 3D game art is created across the industry. From helping with complex tasks like modeling and UV unwrapping to generating realistic textures and simplifying animation retargeting, AI-powered tools are streamlining the production pipeline. This shift is especially beneficial for indie developers and smaller studios, as it frees up valuable time and resources that can be redirected toward creative innovation.
One of the exciting applications of AI lies in assisting concept artists. Advanced AI image generators enable rapid experimentation with styles and designs, allowing artists to quickly visualize unique combinations and fresh ideas. For instance, an artist might blend elements traditionally seen in different art forms to create something entirely new, such as designing a medieval warrior with stylized features inspired by different cultural aesthetics or applying cinematic lighting techniques to fantastical environments.
Character animation has also seen significant advancements thanks to AI. Tasks that once required expensive motion capture setups can now be achieved using consumer-grade cameras and intelligent software. This democratizes high-quality animation, making it accessible to a broader range of creators without compromising on fidelity.
As AI tools continue to improve, they are blurring traditional boundaries in artistic styles and workflows. Whether an artist’s focus is on minimalistic designs or highly realistic visuals, AI empowers creators to explore, combine, and refine their visions with unprecedented flexibility and speed.
Final Words
3D art styles significantly impact the visual appeal of modern video games. Whether it is the realistic visuals of a AAA title or an indie game’s charming low poly style, the art style plays a crucial role in shaping the overall experience.
The five 3D art styles discussed in this article – cartoon, realism, fantasy realism, low poly/cell shading, and hand-painted/stylized – are just a few of the many approaches game developers can take. Each style has its own unique strengths and applications, and the choice of art style ultimately depends on the game’s theme, genre, and target audience.
In addition, a variety of software and technologies are available to help game developers create stunning 3D visuals. From powerful game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine to industry-standard 3D modeling software like Maya and Blender, there are many tools available to help developers bring their artistic vision to life.
Overall, the world of 3D art is constantly evolving, and new trends and techniques will continue to emerge in the years to come. As technology advances and new platforms emerge, it will be fascinating to see how game developers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with 3D art.


